than those who avoid indoor tanning, according to a retrospective study involving 434 melanoma patients.
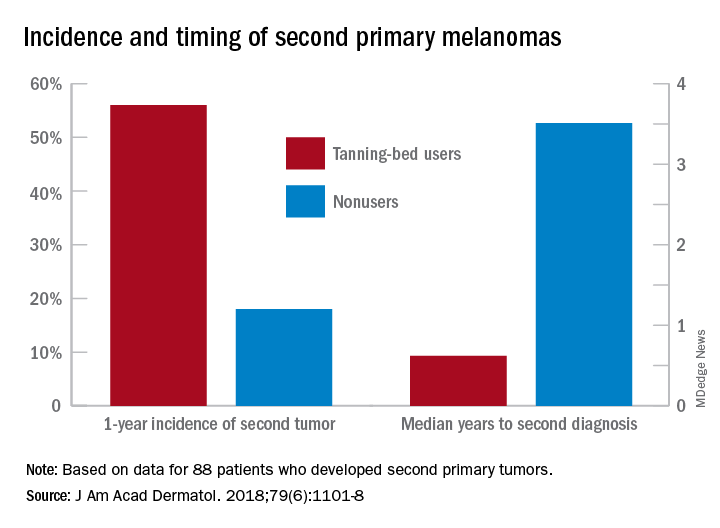
Over the course of the study, 88 patients developed multiple primary melanomas. In the year after the original diagnosis, 56% of the patients exposed to artificial UV radiation (UVR) were diagnosed with a second primary melanoma versus 18% of the nonexposed subjects, Yang Li of Washington University, St. Louis, and her associates said in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.The incidence of second melanomas over the entire 16-year course of the study was 25.2% among the tanning-bed users and 18.6% for nonusers. Among these study subjects – 27 with tanning-bed exposure and 61 without – median time to the second tumor was 225 days (0.62 years) for exposed patients and 1,280 days (3.50 years) for those with no exposure, the investigators reported.
This study, they wrote, is the first to show that “patients who had second primary melanoma diagnoses were more likely to have had” exposure to artificial UVR. The increased radiation intensity of tanning beds, “as opposed to UVR from ambient sunlight, in a physiologically vulnerable patient population [fair-skinned persons] at an early age contributes to our findings of decreased tumor lag time.”
SOURCE: Li Y et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79(6):1101-8.