BALTIMORE – Even in a public health system like Canada’s, almost and researchers have identified patient characteristics that could be predictive of dropout risk that would potentially have implications in a nonuniversal system, such as that of the United States, according to a study of almost 18,000 patients reported at the annual meeting Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons.
“Even in a universal health care system, clear disparities exist among patient populations having bariatric surgery,” said Aristithes Doumouras, MD, of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “Extensive work-ups and long wait times can have an impact on the delivery of bariatric care.”
Dr. Doumouras reported on results of a retrospective, population-based study of 17,703 patients referred for surgery during 2009-2015 in the Ontario Bariatric Network, a province-wide network of 11 hospitals credentialed to perform bariatric surgery. The study found that 23.2% of patients referred for bariatric surgery did not go through with it and that overall average wait times between referral and the operation were just short of a year – 362.2 days to be precise.
The goal of the study was to identify any factors associated with attrition, Dr. Doumouras said.
“Predictors of interest included patient demographics – age, sex, income quintile, immigration status, employment status, smoking status – and comorbidities, such as diabetes, heart failure, hypertension, sleep apnea, and renal disease,” he said. “The study also evaluated health services factors, such as overall wait time to bariatric surgery, presence of centers of excellence, and health care utilization.”
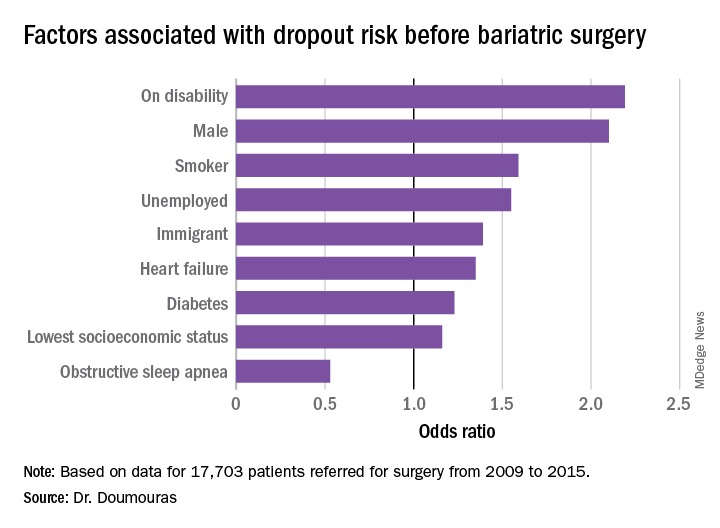
The study found that demographics with more than twice the odds of attrition were male gender and presence of a disability (P less than .01). Smokers were 60% more likely to drop out (P less than .01), he said. “To receive bariatric surgery in Ontario, smokers must go through a smoking cessation program.”
Unemployed individuals and immigrants also had higher rates of attrition, at 55% and 39%, respectively, and were more likely to not go through with the operation (P less than .01). Health factors associated with attrition, but to a lesser extent, were diabetes (odds ratio, 1.23) and heart failure (OR, 1.35; P less than .01).
“Low socioeconomic status actually had a very low impact in our system on attrition after adjustment for other demographic factors such as disability and unemployment,” Dr. Doumouras said, noting a 16% greater risk of attrition in this group (P = .02).
“Interestingly,” he noted, “there was one factor associated with less dropout – obstructive sleep apnea – probably because people hate using the CPAP machines every single night.” People with OSA were 47% less likely to drop out than were people without the disease (P less than .001).
When asked if the findings would be applicable in the United States, Dr. Doumouras said they would to an extent.
“I think we can say confidently that they would apply to most universal health care systems,” he said. “In nonuniversal health care systems, the interplay between insurance status, socioeconomic status, and the like makes it more of a complex relationship, but if you were to take any kind of health care system, even in the United States, you would probably see very similar trends in terms of who can get bariatric surgery.”
He added, “I think also the length of work-up matters. Only a 3- or 4-week work-up probably affects attrition as well. These are relatively universal things.”
Dr. Doumouras has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Doumouras A et al. SAGES 2019, Abstract S118.