Of the 150 patients, 1 died during the follow-up period, leaving 149. Of these, 134 completed the 5-year follow-up. Eight patients in the IMT group and 1 patient in the sleeve gastrectomy group never initiated assigned treatment, and 6 patients were lost to follow-up. One patient from the IMT group and 1 patient from the sleeve gastrectomy group crossed over to the gastric bypass group.
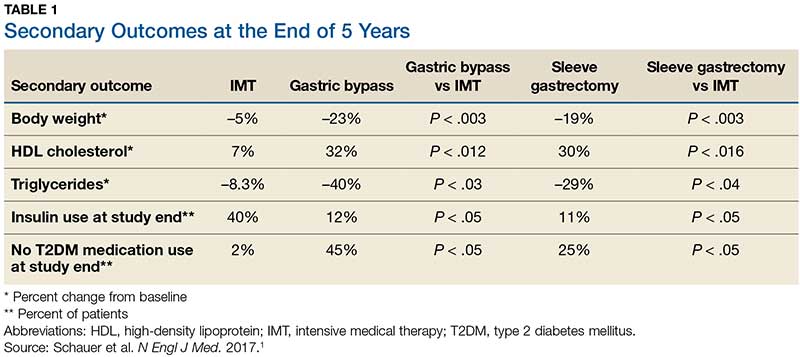
Results. More patients in the bariatric surgery and sleeve gastrectomy groups achieved an A1C of ≤ 6% than in the IMT group (14 of 49 gastric bypass patients, 11 of 47 sleeve gastrectomy patients, and 2 of 38 IMT patients). Compared with those in the IMT group, the patients in the 2 surgery groups showed greater reductions from baseline in body weight and triglyceride levels and greater increases from baseline in HDL cholesterol levels; they also required less antidiabetes medication for glycemic control (see Table).1
WHAT’S NEW?
Big benefits, minimal adverse effects
Prior studies evaluating the effect of gastric bypass surgery on diabetes were observational or had a shorter follow-up duration. This study demonstrates that bariatric surgery plus IMT has long-term benefits with minimal adverse events, compared with IMT alone.1,5 Additionally, this study supports recommendations for bariatric surgery as treatment for T2DM in patients with a BMI ≥ 27, which is below the starting BMI (35) recommended by the ADA.1,4
CAVEATS
Surgery is not without risks
The risk for surgical complications—eg, gastrointestinal bleeding, severe hypoglycemia requiring intervention, and ketoacidosis—in this patient population is significant.1 Other potential complications include gastrointestinal leak, stroke, and infection.1 Additionally, long-term complications from bariatric surgery are emerging and include choledocholithiasis, intestinal obstruction, and esophageal pathology.7 Extensive patient counseling is necessary to ensure that patients make an informed decision regarding surgery.
This study utilized surrogate markers (A1C, lipid levels, and body weight) as disease-oriented outcome measures. Patient-oriented outcomes, such as morbidity and mortality, were not explored in this study.
Continue to: Due to the small sample size...