ANSWER
The correct answer is seborrheic keratosis (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
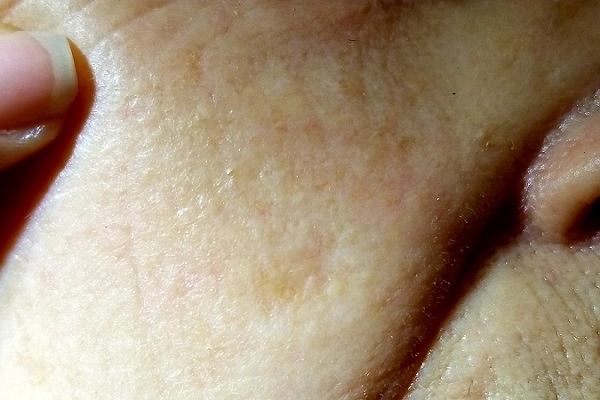
Seborrheic keratosis could not be in the differential because it is, by definition, an epidermal lesion—that is, “stuck on” the surface of the skin. It creates a rough surface that can be easily scraped off. The lesion could have been an actual scar, but other factors (its continuous growth) and the history of excessive ultraviolet exposure pushed us away from including this condition in the differential.
The differential for this patient included sun-caused skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma (BCC; choice “b”), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC; choice “d”), and amelanotic melanoma (choice “c”). These conditions can have a colorless and scar-like appearance, and they also destroy surface adnexae. Therefore, the lack of hairs, pores, or skin lines in a circumscribed area should raise concern for possible skin cancer, especially in at-risk patients such as this one.
BCC (otherwise known as cicatricial basal cell carcinoma) is by far the most common of all sun-caused skin cancers, but it usually presents as an obvious papule or nodule, often with telltale features such as pearly, rolled borders and focal erosion or ulceration. But there are exceptions, and the scar-like BCC is one.
SCC can also occasionally present in this manner, as can amelanotic melanoma, which is a colorless melanoma and very easy to miss. This case perfectly illustrates the point I often make to the students and residents I teach: When skin cancer is suspected, pay at least as much attention to the owner as to the lesion. Also, when in doubt, biopsy will settle the matter.
TREATMENT
For the patient, shave biopsy confirmed the presence of BCC. She was then referred for Mohs micrographic surgery because of the lesion’s size, location, and uncertain visible margins.