A 90-year-old man was admitted from the Emergency Department (ED) to our inpatient service for difficulty urinating and hematuria. In the ED, a complete blood count (CBC) with differential and a urinalysis were performed. CBC showed a mild normocytic anemia, consistent with the patient’s known chronic kidney disease. The urinalysis revealed moderate blood, trace ketones, proteinuria, small leukocyte esterases, positive nitrites, and more than 182 red blood cells—findings suspicious for a urinary tract infection. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis was notable for a soft-tissue mass in the bladder.
He had a history of coronary artery disease (treated with stent placement), atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, hypothyroidism, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a 60-pack-per-year history of tobacco dependence, chronic kidney disease, prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy, peripheral vascular disease, and gout. Medications included digoxin, metoprolol, torsemide, aspirin, levothyroxine, fluticasone, albuterol, omeprazole, diclofenac, escitalopram, and minocycline.
About 5 years earlier, doctors had discovered a popliteal thrombosis that required emergent thrombectomy of the infragenicular popliteal artery, thromboembolectomy of the right posterior tibial artery, graft angioplasty of the right posterior tibial artery, and right anterior fasciotomy for compartment syndrome.
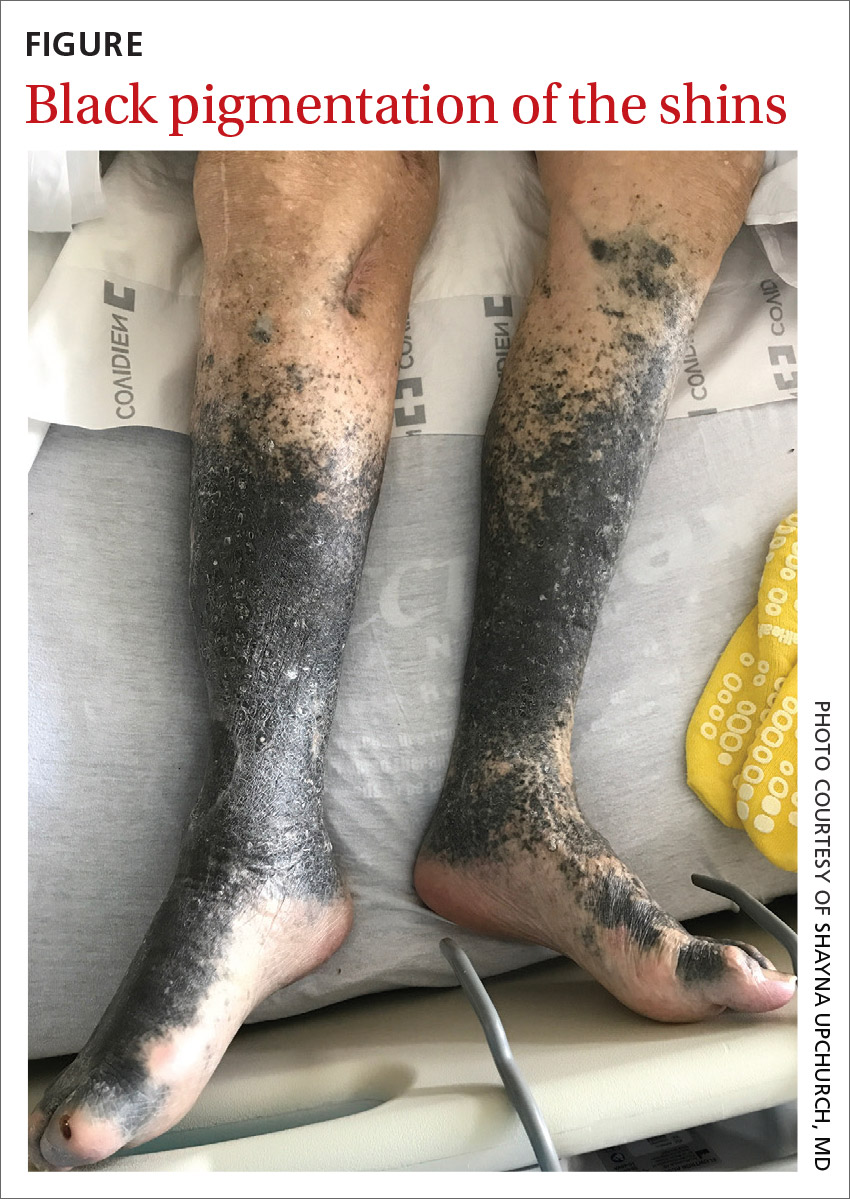
Ten months later, an abscess formed at the incision site. His physician irrigated the popliteal wound and prescribed intravenous (IV) vancomycin. However, the patient developed an allergy and IV daptomycin was initiated and followed by chronic antibiotic suppression with oral minocycline 100 mg bid for about 3.5 years. Skin discoloration appeared within a year of starting the minocycline.
During his hospitalization on our service, we noted black pigmentation of both legs (FIGURE). He had intact strength and sensation in his legs, 1+ pitting edema, no pain upon palpation, and 2+ distal pulses. The patient was well appearing and in no acute distress.