Diagnosis: Kyrle disease
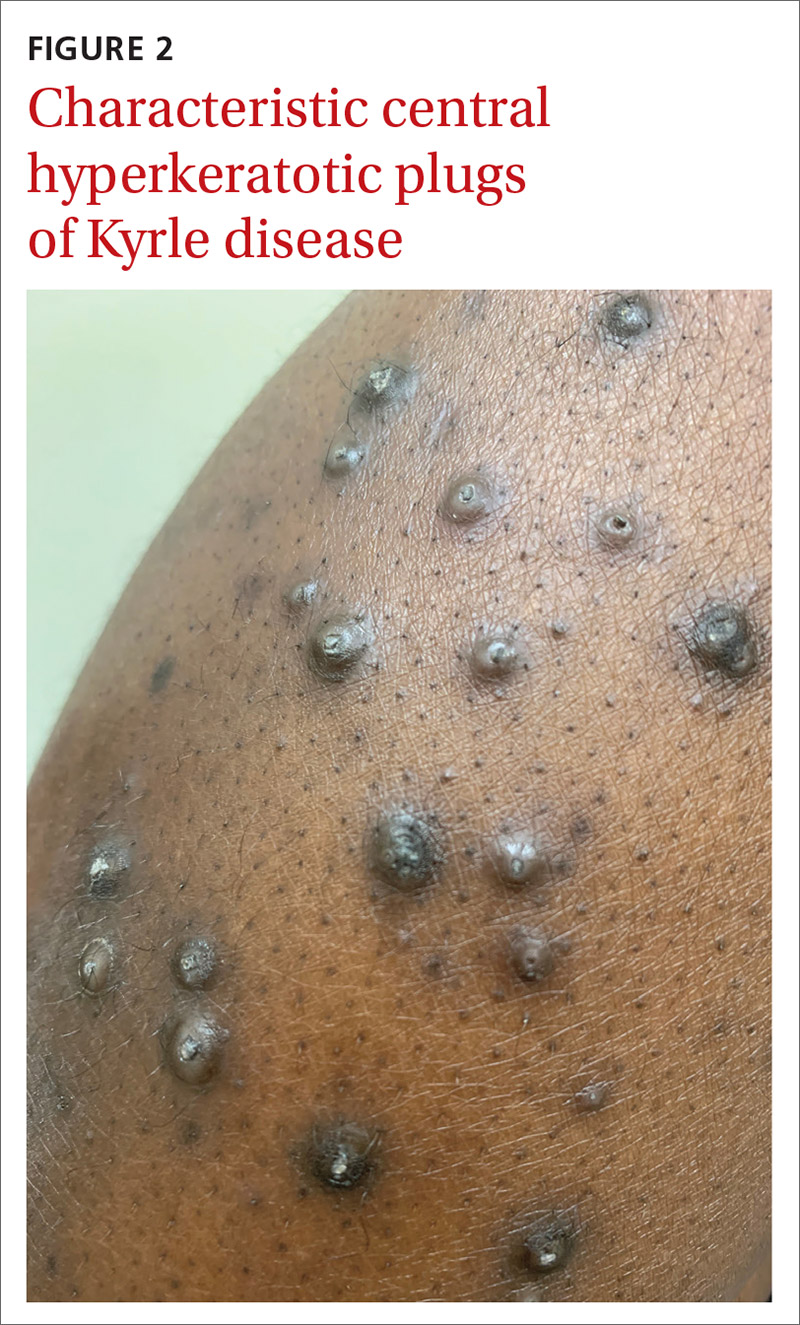
The patient’s end-stage renal disease and type 2 diabetes—along with findings from the physical examination—led us to suspect Kyrle disease. The punch biopsy, as well as the characteristic keratotic plugs (FIGURE 2) within epidermal invagination that was bordered by hyperkeratotic epidermis, confirmed the diagnosis.
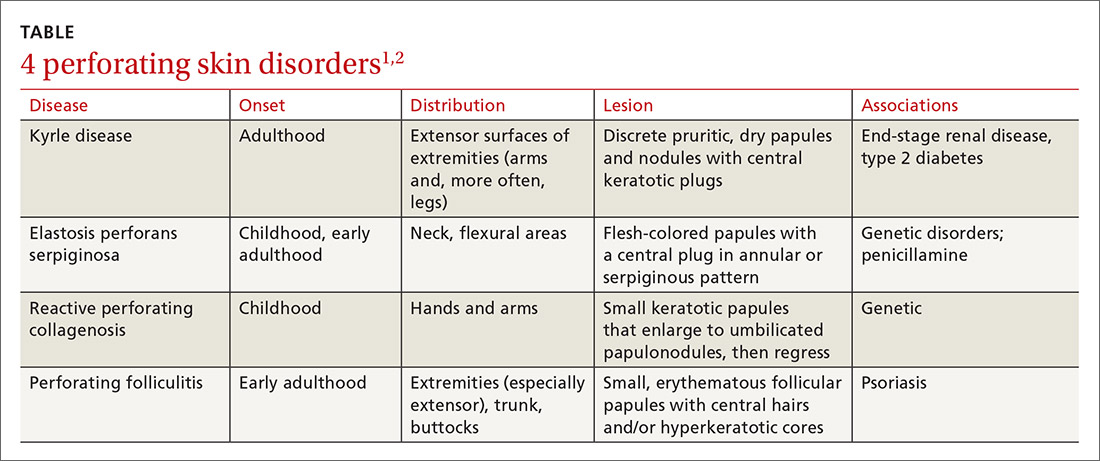
Kyrle disease (also known as hyperkeratosis follicularis et follicularis in cutem penetrans) is a rare skin condition. It is 1 of 4 skin conditions that are classified as perforating skin disorders; the other 3 are elastosis perforans serpiginosa, reactive perforating collagenosis, and perforating folliculitis (TABLE1,2).3 Perforating skin disorders share the common characteristic of transepidermal elimination of material from the upper dermis.4 These disorders are typically classified based on the nature of the eliminated material and the type of epidermal disruption.5
There are 2 forms of Kyrle disease: an inherited form often seen in childhood that is not associated with systemic disease and an acquired form that occurs in adulthood, most commonly among women ages 35 to 70 years who have systemic disease.3,4,6 The acquired form of Kyrle disease is associated with diabetes and renal failure, but there is a lack of data on its pathogenesis.7,8
Characteristic findings include discrete pruritic, dry papules and nodules with central keratotic plugs that are occasionally tender. These can manifest over the extensor surface of the extremities, trunk, face, and scalp.4,7,9 Lesions most commonly manifest on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities.
Other conditions that feature pruritic lesions
In addition to the other perforating skin disorders described in the TABLE,1,2 the differential for Kyrle disease includes the following:
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a skin disorder in which the manifestation of extremely pruritic nodules leads to vigorous scratching and secondary infections. These lesions typically have a grouped and symmetrically distributed appearance. They often appear on extensor surfaces of upper and lower extremities.10 PN has no known etiology, but like Kyrle disease, is associated with renal failure. Biopsy can help to distinguish PN from Kyrle disease.
Continue to: Hypertrophic lichen planus