Clinical Review
Chronic vulvar symptoms and dermatologic disruptions: How to make the correct diagnosis
When a patient reports chronic symptoms, it’s important to look beyond yeast infection and other common causes to accurately identify her...
Some patients experience recurrent ulcers. A second prescription of prednisone can be provided for immediate reinstitution with onset of symptoms. However, frequent recurrences may require ongoing suppressive medication, with dapsone being the usual first choice. Colchicine often is used, and thalidomide and tumor necrosis factor-a blockers (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) also are extremely beneficial. 3,4
CASE 4. INCREASED NEUTROPHILS AND NO LACTOBACILLI
A 36-year-old woman visits your office reporting introital itching, vulvar dysuria, and superficial dyspareunia that have lasted 6 months. She has tried over-the-counter antifungal therapy, with only slight improvement while using the cream. Her health is normal otherwise, lacking pain syndromes or abnormalities suggestive of pelvic floor dysfunction. She experienced comfortable sexual activity until 6 months ago.
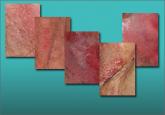
The only abnormalities apparent on physical examination are redness of the vestibule, medial labia minora, and vaginal walls, with edema of the surrounding skin and no oral lesions ( FIGURE 4A ). Copious vaginal secretions are visible at the introitus. A wet mount shows a marked increase in neutrophils with scattered parabasal cells ( FIGURE 4B ). There are no clue cells, lactobacilli, or yeast forms. The patient’s pH level is greater than 6.5. Routine and fungal cultures and molecular studies for chlamydia, trichomonas, and gonorrhea are returned as normal.
Diagnosis: Desquamative inflammatory vaginitis.
Treatment: Clindamycin vaginal cream, 1/2 to 1 full applicator nightly, with a weekly oral fluconazole tablet (200 mg is more easily covered by insurance) to prevent secondary candidiasis. You schedule a follow-up visit in 1 month.
Desquamative inflammatory vaginitis (DIV) is described as noninfectious inflammatory vaginitis in a setting of normal estrogen and absence of skin disease of the mucous membranes of the vagina. The condition is characterized by an increase in white blood cells and parabasal cells, and absent lactobacilli, with relatively high vaginal pH. DIV is thought to represent an inflammatory dermatosis of the vaginal epithelium. 5 Although some clinicians believe that DIV is actually lichen planus, the latter exhibits erosions as well as redness, nearly always affects the mouth and the vulva, and produces remarkable scarring. DIV does not erode, affect any other skin surfaces, or scar.
Other rare skin diseases that produce erosions and scarring also can be ruled out by the presence of erosions, absence of oral disease, and absence of other mucosal involvement. These diseases include cicatricial pemphigoid, pemphigus vulgaris, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Infectious diseases characterized by inflammation are excluded by culture or molecular studies, and atrophic vaginitis and retained foreign bodies (especially retained tampons) can produce a similar picture.
The vulvar itching and irritation that occur with DIV most likely represent an irritant contact dermatitis, with vaginal secretions serving as the irritant.
How to treat DIV
The management of DIV consists of either topical clindamycin cream (theoretically for its anti-inflammatory rather than antimicrobial properties) or intravaginal corticosteroids, especially hydrocortisone acetate. 6 Hydrocortisone can be tried at the low commercially available dose of 25-mg rectal suppositories, which should be inserted into the vagina nightly, or it can be compounded at 100 or 200 mg, if needed. If the condition is recalcitrant, combination therapy can be used.

When a patient reports chronic symptoms, it’s important to look beyond yeast infection and other common causes to accurately identify her...
Arm yourself with these best options for tackling insistent infection
Many cases of generalized vulvodynia and localized vulvodynia (vestibulodynia) are mistakenly attributed to yeast infection, pudendal neuralgia,...
Although the origins of vestibulodynia are incompletely understood, this subset of vulvar pain is manageable and—good news—even curable in some...
