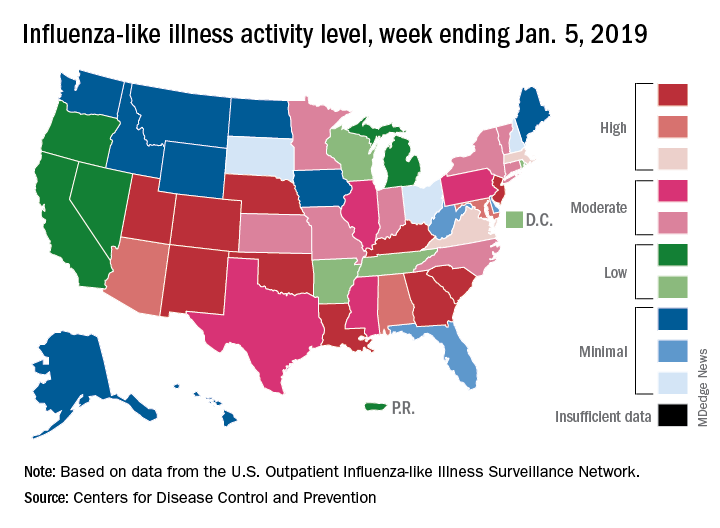
The 2018-2019 flu season may have peaked as measures of influenza-like illness (ILI) activity dropped in the first week of the new year, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The proportion of outpatients visits for ILI dropped to 3.5% for the week ending Jan. 5, 2019, after reaching 4.0% the previous week. Outpatient ILI visits first topped the national baseline of 2.2% during the week ending Dec. 8, 2018, and have remained above that value for 5 consecutive weeks, the CDC’s influenza division said on Jan. 11.
Flu activity reported by the states reflects the national drop: 10 states came in at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of activity for the week ending Jan. 5 – down from 12 the week before – and a total of 15 were in the high range from 8 to 10, compared with 19 the previous week, the CDC said. Two states, Mississippi and Texas, dropped from level 10 to level 7, which the CDC categorizes as moderate activity.
A total of 73 ILI-related deaths were reported during the week ending Dec. 29 (the latest with data available; reporting less than 68% complete), which already exceeds the 71 deaths reported for the week ending Dec. 22 (reporting 85% complete). Flu deaths totaled 437 through the first 13 weeks of the 2018-2019 season, compared with the 1,659 that occurred during weeks 1-13 of the very severe 2017-2018 season, CDC data show.
For the week ending Jan. 5, the CDC received reports of three flu-related pediatric deaths, all of which occurred the previous week. For the season so far, there have been 16 pediatric deaths, compared with 20 at this point in the 2017-2018 season.
Estimates released during the flu season for the first time show that between 6 and 7 million Americans have been infected since Oct. 1, 2018, and that 69,000-84,000 people have been hospitalized with the flu through Jan. 5, 2019. These cumulative totals have previously been available only at the end of the season, the CDC noted.