according to the Consumer Product Safety Commission.
Of the estimated 9,100 fireworks-related injuries treated in emergency departments last year, 5,600 (62%) occurred between June 22 and July 22, 2018. That works out to a rate of 1.7 ED-treated injuries per 100,000 people for that 1 month and a rate of 2.8 per 100,000 for the entire year, the CPSC said in its 2018 Fireworks Annual Report.
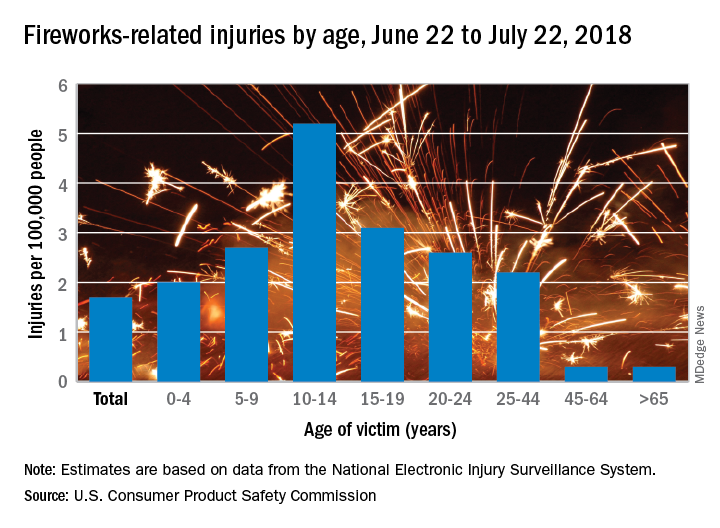
Children had higher injury rates than adults in the Fourth of July window, and those aged 10-14 years had the highest rate of all, 5.2 injuries per 100,000 population. They were followed by teens aged 15-19 years (3.1 per 100,000) and children aged 5-9 (2.7 per 100,000), the CPSC investigators said based on data from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System.
A deeper dive into the data pool shows that firecrackers caused more injuries – 19% of the total for the month – than any other type of firework device (reloadable shells were second at 12%). Burns were the most common type of injury, making up 44% of the total, and hands and fingers were the body parts most often injured (28% of the total), they reported.
There were five fireworks-related deaths last year – below the average of 7.6 per year since 2003 – but the total for 2018 may go up because reporting for the year is not yet complete. In one of the 2018 cases, an 18-year-old taped a tube to a football helmet and tried to launch a mortar shell while wearing the helmet. The first one worked, but the second shell got stuck and exploded in the tube, the CPSC said.
“CPSC works year-round to help prevent deaths and injuries from fireworks, by verifying fireworks meet safety regulations in our ports, marketplace, and on the road,” acting CPSC Chairman Ann Marie Buerkle said in a written statement. “Beyond CPSC’s efforts, we want to make sure everyone takes simple safety steps to celebrate safely with their family and friends.”