“There’s rue for you, and here’s some for me; we may call it herb of grace o’ Sundays. O, you must wear your rue with a difference.”
— Ophelia in Hamlet by William Shakespeare
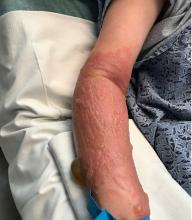
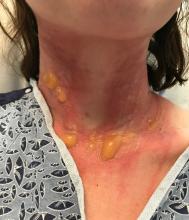
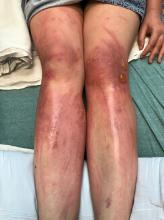
The patient was admitted to the hospital for IV fluids, pain control, and observation. The following day she admitted using the leaves of a plant on the trail as a bug repellent, as one time was taught by her grandfather. She rubbed some of the leaves on the brother as well. The grandfather shared some pictures of the bushes, and the plant was identified as Ruta graveolens.
The blisters were deroofed, cleaned with saline, and wrapped with triamcinolone ointment and petrolatum. The patient was also started on a prednisone taper and received analgesics for the severe pain.
Ruta graveolens also known as common rue or herb of grace, is an ornamental plant from the Rutaceae family. This plant is also used as a medicinal herb, condiment, and as an insect repellent. If ingested in large doses, it can cause severe abdominal pain and vomiting. It also can be hepatotoxic.
The herb contains furocumarines, such as 8-methoxypsoralen and 5-methoxypsoralen and furoquinoline alkaloids. These chemicals when exposed to UVA radiation cause cell injury and inflammation of the skin. This is considered a phototoxic reaction of the skin, compared with allergic reactions, such as poison ivy dermatitis, which need a prior sensitization to the allergen for the T cells to be activated and cause injury in the skin. Other common plants and fruits that can cause phytophotodermatitis include citrus fruits, figs, carrots, celery, parsnips, parsley, and other wildflowers like hogweed.
Depending on the degree of injury, the patients can be treated with topical corticosteroids, petrolatum wraps, and pain control. In severe cases like our patient, systemic prednisone may help stop the progression of the lesions and help with the inflammation. Skin hyperpigmentation after the initial injury may take months to clear, and some patient can develop scars.
The differential diagnosis should include severe bullous contact dermatitis like exposure to urushiol in poison ivy; second- and third-degree burns; severe medications reactions such Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, and inmunobullous diseases such as bullous lupus erythematosus, pemphigus vulgaris, or bullous pemphigoid. If there is no history of exposure or there are any other systemic symptoms, consider performing a skin biopsy of one of the lesions.
In this patient’s case, the history of exposure and skin findings helped the dermatologist on call make the right diagnosis.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
J Burn Care Res. 2018 Oct 23;39(6):1064-6.