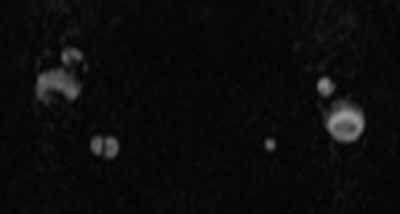
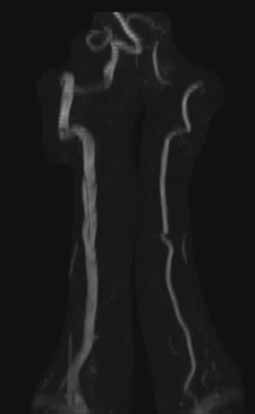
A 41-year-old-man with a history of hypertension presented to the ED with a sudden onset of severe occipital headache and unstable gait. On physical examination, right-sided ptosis and miosis (Horner’s syndrome) were noted. An emergent head computed tomography (CT) scan was performed and showed no evidence of hemorrhage or infraction. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of the head and neck were also ordered. Noncontrast MRA images of the neck are shown above (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
What is the diagnosis?
What other imaging modalities may be useful for evaluation?
Dr Wladyka is an assistant professor of radiology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City and an assistant attending radiologist at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. Dr Hentel is an associate professor of clinical radiology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City. He is also chief of emergency/musculoskeletal imaging and the executive vice-chairman for the department of radiology at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. He is associate editor, imaging, of the EMERGENCY MEDICINE editorial board.