Methods
After obtaining institutional review board approval (16-H192), females who screened positive for a history of MST, using the validated MST screening questionnaire, were recruited from the Women’s Continuity Clinic, Urology clinic, and via a research flyer placed within key locations at the New Mexico Veterans Affairs (VA) Health Care System (NMVAHCS).11 Inclusion criteria were veterans aged > 18 years who could speak and understand English. Those who agreed to participate attended any 1 of 5 focus groups. Prior to initiation of the focus groups, the investigators generated a focus-group script, including specific questions or probes to explore treatment, unmet needs (such as other health conditions the veteran associated with MST that were not being addressed), and recommendations for care improvement.
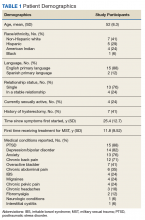
Subjects granted consent privately prior to conduction of the focus group. Each participant completed a basic demographic (age, race, ethnicity) and clinical history (including pain conditions and therapy received for MST). These characteristics were evaluated with descriptive statistics, including means and frequencies.
The focus groups took place on the NM VAHCS Raymond G. Murphy VA Medical Center campus in a private conference room and were moderated by nonmedical research personnel experienced in focus-group moderation. Focus groups were recorded and transcribed. An iterative process was used with revisions to the script and probe questions as needed. Focus groups were planned for 2 hours but were allowed to continue at the participants’ discretion.
The de-identified transcripts were uploaded to the web-based qualitative engine Dedoose 6.2.21 software (Los Angeles, CA) and coded. Using grounded theory, the codes were grouped into themes and subsequently organized into emergent concepts.8,12 Following constant comparative methodology, ideas were compared and combined between each focus group.8,13 After completion of the focus groups, the generated ideas were organized and refined to create a conceptual framework that represented the collective ideas from the focus groups.
Results
Between January and June 2017, 5 focus groups with 17 participants were conducted; each session lasted about 3 hours. The average age was 52 ± 8.3 years, and were from a diverse racial and ethnic background. Most reported that > 20 years had passed since the first MST, and care-seeking for the first time was > 11 years after the trauma, although symptoms related to the MST most frequently began within 1 year of the trauma (Table 1).
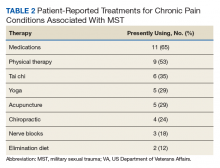
The majority (11/17) had participated in some sort of traditional treatment for MST, such as medications, group therapy and/or private counseling. Many females were using alternative therapies for treating pain conditions associated with MST (Table 2).14Preliminary Themes
The Trauma
Focus-group participants noted improved therapies offered by the VA but challenges obtaining health care:
“…because I’m really trying to deal with it and just be happy and get my joy back and deal with the isolation.”
“Another way that the memories affected me was barricading myself in my own house, starting from the front door.”
Male-Dominated VA
Participants also noted that, along with screening improving the system, dedicated female staff and service connection are important: