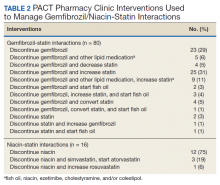
Of the 107 patients referred to the PACT Pharmacy Clinic, 80 (74.8%) had TG laboratory results available and were included in the analysis. These patients were followed by the PACT CPS until the drug interaction was resolved and confirmed to have TG levels at goal (< 500 mg/dL). Gemfibrozil doses ranged from 300 mg daily to 600 mg twice daily, with 70% (n = 56) of patients taking 600 mg twice daily. The PACT CPS made 148 interventions (Table 2). Twenty-three (29%) patients required only gemfibrozil discontinuation. The remaining 57 patients (71%) required at least 2 medication interventions. The PACT CPS generated 213 encounters for resolving drug interactions with a median of 2 encounters per patient.
Quality assurance review identified 5 patients (5.3%) who underwent gemfibrozil discontinuation by protocol, despite having criteria that would have recommended against discontinuation. In accordance with the protocol criteria, these patients were later referred to the PACT Pharmacy Clinic. None of these patients experienced a TG increase at or above the threshold of 500 mg/dL after gemfibrozil was initially discontinued but were excluded from the earlier analysis.
Niacin-Statin Interactions
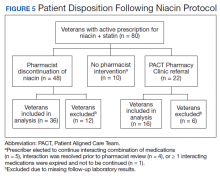
Pharmacists discontinued niacin by protocol for 48 patients (60.0%), and 22 patients (27.5%) were referred to the PACT Pharmacy Clinic (Figure 5). For the remaining 5 patients (6.3%), the interaction was either addressed outside the protocol prior to pharmacist review, or an interacting prescription was expired and not to be continued. Additionally, niacin was continued per prescriber preference in 5 patients (6.3%).
Thirty-six patients (75%) had TG laboratory results available following niacin discontinuation by protocol and were included in the analysis. Most patients’ (n = 33, 91.7%) TG levels decreased or increased by < 100 mg/dL. No patient had a TG level that increased higher than the threshold of 500 mg/dL. The mean (SD) time to the first laboratory result after the pharmacists mailed the notification letter, was 5.3 (2.5) months (range, 1.2-9.8). The pharmacists spent a mean of 15 minutes per patient resolving each interaction. The quality assurance review found no discrepancies in the pharmacists’ application of the protocol.
Of the 22 patients referred to the PACT Pharmacy Clinic, 16 (72.7%) patients had TG laboratory results available and were included in the analysis. As with the gemfibrozil interactions, these patients were followed by the PACT Pharmacy Clinic until the drug interaction was resolved and confirmed to have TGs at goal (< 500 mg/dL). Niacin doses ranged from 500 mg daily to 2,000 mg daily, with the majority of patients taking 1,000 mg daily. The PACT CPS made 23 interventions. The PACT CPS generated 46 encounters for resolving drug interactions with a median of 2 encounters per patient.
Discussion
Following gemfibrozil or niacin discontinuation by protocol, most patients with available laboratory results experienced either a decrease or modest TG elevation. The proportion of patients experiencing a decrease in TGs was unexpected but potentially multifactorial. Individual causes for the decrease in TGs were beyond the scope of this analysis. The retrospective design limited the ability to identify variables that could have impacted TG levels when gemfibrozil or niacin were started and discontinued. Although the treatment of TG levels is not indicated until it is ≥ 500 mg/dL, due to an increased risk of pancreatitis, both protocols excluded patients with a history of TGs ≥ 400 mg/dL. 19 The lower threshold was set to compensate for anticipated increase in TG levels, following gemfibrozil or niacin discontinuation, and to minimize the number of patients with TG levels ≥ 500 mg/dL. The actual impact on patients’ TG levels supports the use of this lower threshold in the protocol.