Naltrexone reduces the risk for hospitalization for alcohol use disorder (AUD), regardless of whether it is used alone or in conjunction with disulfiram or acamprosate, research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 10-year data on more than 125,000 Swedish residents with AUD and found that naltrexone, used as monotherapy or combined with acamprosate or disulfiram, was associated with significantly lower risk for AUD hospitalization or all-cause hospitalization in comparison with patients who did not use AUD medication. The patients ranged in age from 16 to 64 years.
By contrast, benzodiazepines and acamprosate monotherapy were associated with increased risk for AUD hospitalization.
“The take-home message for practicing clinicians would be that especially naltrexone use is associated with favorable treatment outcomes and should be utilized as part of the treatment protocol for AUD,” study investigator Milja Heikkinen, MD, specialist in forensic psychiatry and addiction medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, told this news organization.
On the other hand, “benzodiazepines should be avoided and should not be administered other than for alcohol withdrawal symptoms,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 4 in Addiction.
Real-world data
Previous research has shown that disulfiram, acamprosate, naltrexone, and nalmefene are efficacious in treating AUD, but most studies have been randomized controlled trials or meta-analyses, the authors write.
“Very little is known about overall health outcomes (such as risks of hospitalization and mortality) associated with specific treatments in real-world circumstances,” they write.
“The study was motivated by the fact that, although AUD is a significant public health concern, very little is known, especially about the comparative effectiveness of medications indicated in AUD,” said Dr. Heikkinen.
who had been diagnosed with AUD (62.5% men; mean [standard deviation] age, 38.1 [15.9] years). They followed the cohort over a median of 4.6 years (interquartile range, 2.1-.2 years).
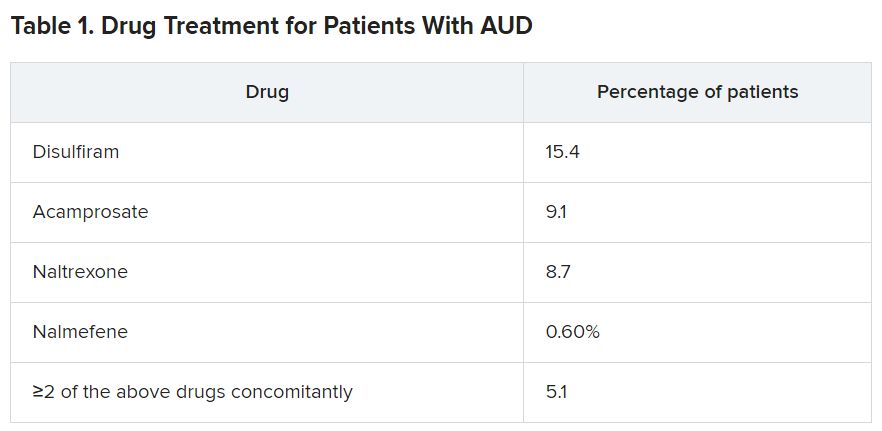
During the follow-up period, roughly one-fourth of patients (25.6) underwent treatment with one or more drugs.
The main outcome measure was AUD-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes were hospitalization for any cause and for alcohol-related somatic causes; all-cause mortality; and work disability.
Two types of analyses were conducted. The within-individual analyses, designed to eliminate selection bias, compared the use of a medication to periods during which the same individual was not using the medication.
Between-individual analyses (adjusted for sex, age, educational level, number of previous AUD-related hospitalizations, time since first AUD diagnosis, comorbidities, and use of other medications) utilized a “traditional” multivariate-adjusted Cox hazards regression model.
AUD pharmacotherapy ‘underutilized’
Close to one-fourth of patients (23.9%) experienced the main outcome event (AUD-related hospitalization) during the follow-up period.
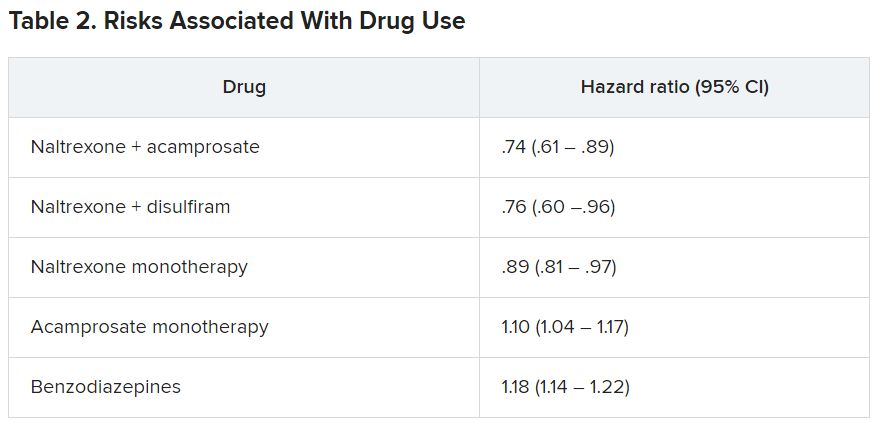
The within-individual analysis showed that naltrexone – whether used as monotherapy or adjunctively with disulfiram or acamprosate – “was associated with a significantly lower risk of AUD-related hospitalization, compared to those time periods in which the same individual did not use any AUD medication,” the authors report.
By contrast, they state, acamprosate monotherapy and benzodiazepines were associated with a significantly higher risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
Similar results were obtained in the between-individual analysis. Longer duration of naltrexone use was associated with lower risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
The pattern was also found when the outcome was hospitalization for any cause. However, unlike the findings of the within-individual model, the second model found that acamprosate monotherapy was not associated with a higher risk for any-cause hospitalization.
Polytherapy, including combinations of the four AUD medications, as well as disulfiram monotherapy were similarly associated with lower risk for hospitalization for alcohol-related somatic causes.
Of the overall cohort, 6.2% died during the follow-up period. No association was found between disulfiram, acamprosate, nalmefene, and naltrexone use and all-cause mortality. By contrast, benzodiazepine use was associated with a significantly higher mortality rate (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.19).
“AUD drugs are underutilized, despite AUD being a significant public health concern,” Dr. Heikkinen noted. On the other hand, benzodiazepine use is “very common.”