This is the third article in the series, "Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia." The remaining articles are Introduction; Presentation and History; Treatment/Management; and References.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of HIT is determined by combining clinical and serologic assessment. HIT should be suspected in any patient who is in day 5 to 14 of heparin therapy and experiences a drop in platelet count of at least 50%, or in whom a new thrombotic event occurs (even if the patient is no longer receiving heparin therapy). The interpretation of all diagnostic information must be made in the context of the patient's clinical probability of HIT.15
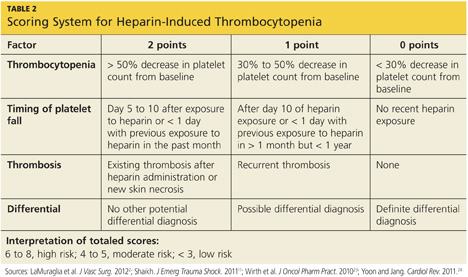
A scoring system referred to as the 4Ts (thrombocytopenia, timing of platelet fall, thrombosis or other sequelae, and test interpretation) is used to help determine the patient's probability of HIT5,21,22 (similar to the scoring strategy shown in Table 22,11,23,24). The patient diagnosed with HIT must be positive for HIT antibodies and meet at least one additional criterion:
• A platelet count decrease of 30% to 50% below baseline, regardless of the actual value
• A venous or arterial thrombosis
• A skin lesion at the heparin injection site; and/or
• An anaphylactic reaction after IV bolus administration of heparin.15
This is the third article in the series, "Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia." The remaining articles are Introduction; Presentation and History; Treatment/Management; and References.
