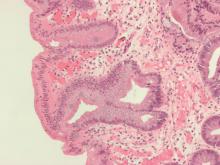
Wide-area transepithelial sampling with 3D (WATS-3D) analysis increased detection of dysplasia when used as an adjunct to the Seattle forceps biopsy protocol in patients with Barrett’s esophagus, according to a recent meta-analysis. While the findings demonstrate potential for increased dysplasia detection, the analysis failed to identify the clinical significance of this detection.
Despite its ability to evaluate Barrett’s esophagus segments and examine targeted biopsies of mucosal abnormalities, the Seattle protocol is primarily limited by lack of adherence and increased risk of sampling error. “Moreover, the rates of ‘missed’ dysplasia and EAC [esophageal adenocarcinoma] remain high, with up to a quarter of all EAC being ‘missed,’ ” wrote study authors Don Codipilly, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, and colleagues. The report is in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
There are challenges associated with the Seattle protocol, specifically poor protocol adherence and missed identification of subtle abnormalities potentially harboring dysplasia. In contrast, the novel WATS-3D may overcome issues related to sampling error due to its ability to obtain higher proportions of Barrett’s esophagus mucosa through the use of a brush-only technique. According to the researchers, previous studies suggest WATS-3D may increase dysplasia yield by approximately 40% compared with conventional surveillance methods.
To gauge the incremental yield of WATS-3D for dysplasia detection compared with the Seattle forceps biopsy protocol, Dr. Codipilly and colleagues performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of seven studies using the two techniques from 2000 to 2020. The researchers defined “incremental yield” of detected dysplasia as a composite of indefinite for dysplasia, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia (HGD), and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). They also compared the two surveillance techniques in terms of incremental yields of HGD/EAC, as well as the rate of reconfirmation of WATS-3D dysplasia on subsequent forceps biopsies.
The seven studies in the final analysis included a pooled cohort of 3,206 patients. According to the meta-analysis, forceps biopsies diagnosed dysplasia in 15.9% (95% confidence interval, 5.4-30.5) of all cases, while the incremental yield of WATS-3D was 7.2% (95% CI, 3.9-11.5). In the pooled analysis of six studies that reported the secondary outcomes, forceps biopsies diagnosed HGD/EAC in 2.3% (95% CI, 0.6-5.1) of patients, while the incremental yield with WATS-3D was 2.1% (95% CI, 0.4-5.3). The researchers point out that WATS-3D was negative in 62.5% of cases where forceps biopsies detected dysplasia. Reports from two of the studies reconfirmed WATS-3D dysplasia with forceps biopsies histology in 20 patients.
“Based on these findings, it cannot be recommended to replace the Seattle Protocol but instead to use both techniques in conjunction to detect dysplasia most effectively,” Omar Awais, DO, assistant professor of surgery in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, said in an email to this news organization.
Dr. Awais, who was not involved in the meta-analysis, suggests further prospective, randomized studies are needed to confirm the results. “Additionally, we will also need studies to show cost-effectiveness for using WATS-3D in addition to Seattle protocol, as these may help verify WATS-3D dysplasia by standard endoscopic protocol and show we are not missing dysplasia using the technique,” he said.
Felice H. Schnoll-Sussman, MD, professor of clinical medicine and director of the Jay Monahan Center for Gastrointestinal Health at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Medical College, added that the meta-analysis “adds to our understanding” of the place of WATS as an adjunct approach in dysplasia detection. “In spite of the rigid selection of studies, this analysis also leaves us with questions about the overall utility of WATS given the lack of follow-up cases where dysplasia was only identified on the WATS brush as well as the overall cost-effectiveness of this approach,” she said.
Dr. Schnoll-Sussman, who was not involved in the study conducted by Dr. Codipilly and colleagues, told this news organization that one of the issues with the WATS brush is obtaining adequate sampling, which may impede adherence. “Attention has to be paid to sampling all quadrants with the brush, which at times may be challenging, especially in esophagi that are tortuous, angulated, or dilated,” she explained. “Like with any endoscopic technique, care must be taken to obtain high-yield sampling.”
Dr. Schnoll-Sussman noted that the subtle, small areas of denuded mucosa left where the brush has made appropriate contact with the mucosa should be appreciated during sampling. “Taking one’s time to sample the esophageal lining – a major reason for missed lesions in the Seattle protocol – can also become an issue with WATS,” she added.
The study researchers reported conflicts of interest with several pharmaceutical companies. No funding was reported for the study. Dr. Awais and Dr. Schnoll-Sussman had no conflicts to disclose.
Help your patients better understand the risks, testing and treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus by sharing education from the AGA GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/BE.