ROME – Half of all women who experience a first unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE) can safely be spared lifelong anticoagulation through application of the newly validated HERDOO2 decision rule, Marc A. Rodger, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We’ve validated that a simple, memorable decision rule on anticoagulation applied at the clinically relevant time point works. And it is the only clinical decision rule that has now been prospectively validated,” said Dr. Rodger, professor of medicine, chief and chair of the division of hematology, and head of the thrombosis program at the University of Ottawa.
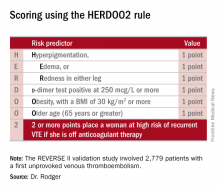
He presented the results of the validation study, known as the REVERSE II study, which included 2,779 patients with a first unprovoked VTE at 44 centers in seven countries. The full name of the decision rule is “Men Continue and HERDOO2,” a name that says it all: the rule posits that all men as well as those women with a HERDOO2 (Hyperpigmentation, Edema, Redness, d-dimer, Obesity, Older age, 2 or more points) score of at least 2 out of a possible 4 points need to stay on anticoagulation indefinitely because their risk of a recurrent VTE off-therapy clearly exceeds that of a bleeding event on-therapy. In contrast, women with a HERDOO2 score of 0 or 1 can safely stop anticoagulation after the standard 3-6 months of acute short-term therapy.
“Sorry, gentlemen, but we could find no low-risk group of men. They were all high risk,” he said. “But 50% of women with unprovoked vein blood clots can be spared the burdens, costs, and risks of lifelong blood thinners.”
Dr. Rodger and coinvestigators began work on developing a multivariate clinical decision rule in 2001. They examined 69 risk predictors, eventually winnowing down to a manageable four potent risk predictors identified by the acronym HERDOO2.
The derivation study was published 8 years ago (CMAJ. 2008;Aug 26;179[5]:417-26). It showed that women with a HERDOO2 score of 2 or more as well as all men had roughly a 14% rate of recurrent VTE in the first year after stopping anticoagulation, while women with a score of 0 or 1 had about a 1.6% risk. The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis suggests that it’s safe to discontinue anticoagulants if the risk of recurrent thrombosis at 1 year off-therapy is less than 5%, given the significant risk of serious bleeding on-therapy and the fact that a serious bleed event is two to three times more likely than a VTE to be fatal.
Dr. Rodger and coinvestigators recognized that a clinical decision rule needs to be externally validated before it’s ready for prime-time use in clinical practice. Thus, they conducted the REVERSE II study, in which the decision rule was applied after the 2,799 participants had been on anticoagulation for 5-12 months. All had a first proximal deep vein thrombosis and/or a segmental or greater pulmonary embolism. Patients were still on anticoagulation at the time the rule was applied, which is why the cut point for a positive d-dimer test in HERDOO2 is 250 mcg/L, half of the threshold value for a positive test in patients not on anticoagulation.
They identified 631 women as low risk, with a HERDOO2 score of 0 or 1. They and their physicians were instructed to stop anticoagulation at that time. The 2,148 high-risk subjects – that is, all of the men and the high-risk women – were advised to remain on anticoagulation. The primary study endpoint was the rate of recurrent VTE in the 12 months following testing and patient guidance. The lost-to-follow-up rate was 2.2%.
The recurrent VTE rate was 3% in the 591 low-risk women who discontinued anticoagulants and zero in 31 others who elected to stay on medication. In the high-risk group identified by the HERDOO2 rule, the recurrent VTE rate at 12 months was 8.1% in the 323 who opted to discontinue anticoagulants and just 1.6% in 1,802 who continued on therapy as advised, a finding that underscores the effectiveness of selectively applied long-term anticoagulation therapy, he continued.
The recurrent VTE rate among the 291 women with a HERDOO2 score of 0 or 1 who were on exogenous estrogen was 1.4%, while in high-risk women taking estrogen the rate was more than doubled at 3.1%. But in women aged 50-64 identified by the HERDOO2 rule as being low risk, the actual recurrent VTE rate was 5.7%, a finding that raised a red flag for the investigators.