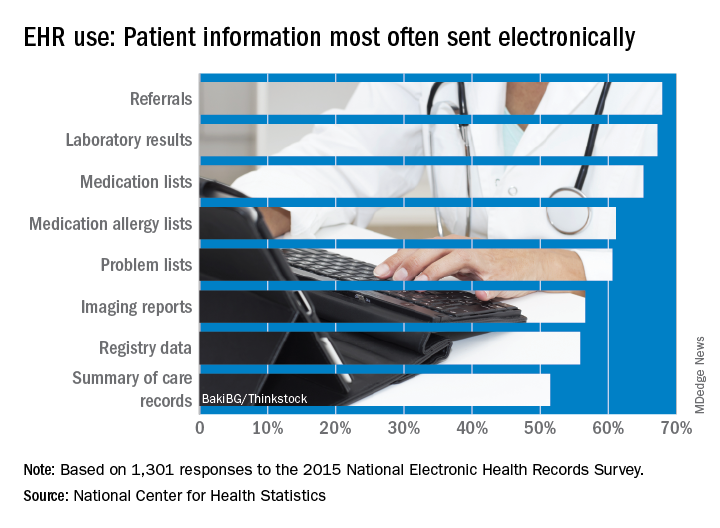
Office-based physicians who have electronic health records are most likely to send patient health information (PHI) in the form of referrals and laboratory results and receive it as lab results and imaging reports, according to national estimates of electronic PHI using four aspects of interoperability.
Those aspects of sharing PHI are sending, receiving, integrating, and searching. With federal estimates of EHR adoption at 78% for office-based physicians, data from the 2015 National Electronic Health Records Just over 65% are sending medication lists electronically, 61% are sending medication allergy lists, and almost 61% are sending problem lists, Ninee S. Yang, PhD, and her associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in National Health Statistics Reports.
Communication in the other direction showed a somewhat different distribution. Of the 1,525 physicians who reported receiving PHI electronically, 79% were the recipients of laboratory results, with imaging reports well behind at 61%, followed by medication lists and referrals at 54% and summary of care records at 52%, the investigators reported.
The ability to integrate information into an EHR – reported by 959 survey respondents – is another key element of interoperability, and 73% of those physicians said that they could integrate lab results into their systems. Other types of PHI, however, did not fare as well: imaging reports came in at 50%, hospital discharge summaries at 49%, summary of care records at 41%, and emergency department notifications at 40%, Dr. Yang and her associates said.
The fourth aspect of interoperability, ability to search for PHI from sources outside the practice, was reported by 1,335 respondents in 2015, with 90% looking for medication lists, 88% for medication allergy lists, 80% for hospital discharge summaries, 59% for imaging reports, and 49% for lab results, they said.
These first national estimates of PHI type will be used as baseline data “in tracking progress outlined in the federal plan for achieving interoperability” among physicians with EHR systems, Dr. Yang and her associates wrote.
SOURCE: Yang NS et al. Natl Health Stat Report. 2018 Aug 15;(115):1-9.