The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning healthcare professionals not to use Treanda (bendamustine hydrochloride) solution with closed-system transfer devices (CSTD), adapters, and syringes containing polycarbonate or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS).
Most marketed CSTDs contain either polycarbonate or ABS. And these materials dissolve when they come into contact with N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMA), an ingredient in Treanda solution.
This can lead to device failure, possible product contamination, and potential serious adverse health consequences, including skin reactions in healthcare professionals preparing and administering this product and the risk of small blood vessel blockage in patients.
Discovering the incompatibility
Treanda, which is manufactured by Teva, is used to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has progressed during or within 6 months of treatment with rituximab or a rituximab-containing regimen.
Treanda is available as a solution—Treanda Injection (45 mg/0.5 mL or 180 mg/2 mL solution)—and a lyophilized powder—Treanda for Injection (25mg/vial or 100 mg/vial lyophilized powder).
The incompatibility of DMA with polycarbonate and ABS is only an issue with Treanda solution—not the lyophilized powder.
Since December 2014, Teva has received 40 complaints of the incompatibility issue, which was recently brought to the FDA’s attention. The agency also received a notification of device incompatibility with Treanda solution from a pharmacist.
These incompatibility issues included leaking of the CSTD, breaking or operational failure of the CSTD components, and a cloudy appearance or presence of particulate matter in the intravenous bag after dilution. To date, no adverse events have been reported related to the incompatibility.
FDA recommendations
The FDA has required label changes for both the solution and the powder formulations of Treanda to reflect the following safe preparation information.
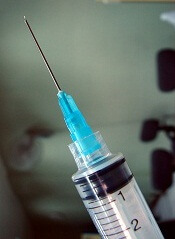
The agency is recommending that healthcare professionals use Treanda solution only with polypropylene syringes containing a metal needle and a polypropylene hub. Polypropylene syringes are translucent in appearance.
Treanda solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever the solution and container permit. The solution must be withdrawn and transferred for dilution in a biosafety cabinet or containment isolator.
If they aim to use a CSTD with Treanda solution, healthcare professionals should verify with the CSTD manufacturer or Teva US Medical Information (1-800-896-5855) that the CSTD is compatible with Treanda solution before preparing the drug.
Alternatively, healthcare professionals can use Treanda lyophilized powder with a CSTD. The solution and lyophilized powder formulations of Treanda should not be mixed.
For additional details on safe preparation of Treanda solution and lyophilized powder, see Teva’s Dear Health Care Provider letter.
Adverse events or quality problems associated with the use of Treanda products can be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.