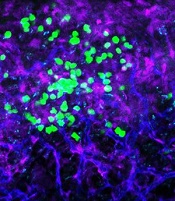
with blood vessels (blue).
Image courtesy of
UC San Diego Health
Preclinical research suggests the cell surface molecule CD98 promotes acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and the anti-CD98 antibody IGN523 can inhibit AML growth.
In AML patient cells and mouse models of the disease, IGN523 disrupted the interactions between leukemia cells and the surrounding blood vessels, thereby inhibiting the growth of AML.
Tannishtha Reya, PhD, of the University of California San Diego School of Medicine, and her colleagues reported these findings in Cancer Cell.
The team believes their results suggest IGN523 or other anti-CD98 antibodies might be useful for treating AML, particularly in children.
However, in a phase 1 study presented at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting, IGN523 demonstrated only modest anti-leukemic activity in adults with AML.
Still, the researchers involved in the phase 1 study said IGN523 may prove effective in combination with other drugs used to treat AML.
Cancer Cell study
“To improve therapeutic strategies for [AML], we need to look not just at the cancer cells themselves but also at their interactions with surrounding cells, tissues, molecules, and blood vessels in the body,” Dr Reya said.
“In this study, we identified CD98 as a critical molecule driving AML growth. We showed that blocking CD98 can effectively reduce leukemia burden and improve survival by preventing cancer cells from receiving support from the surrounding environment.”
Dr Reya’s team engineered mouse models that lacked CD98 and found that loss of this molecule blocked AML growth and improved survival. Furthermore, CD98 loss largely spared normal blood cells, which the researchers said indicates a potential therapeutic window.
Additional experiments revealed that leukemia cells lacking CD98 had fewer stable interactions with the lining of blood vessels—interactions that were needed to fuel AML growth.
So the researchers decided to test the effects of blocking CD98 with a therapeutic inhibitor—IGN523. The team found that IGN523 blocks CD98’s AML-promoting activity in mouse models and human AML cells.
The researchers also transplanted patient-derived AML cells into mice and treated the recipients with either IGN523 or a control antibody. Anti-CD98 treatment effectively eliminated AML cells, while AML in the control mice expanded more than 100-fold.
“This study suggests that human AML can’t get established without CD98 and that blocking the molecule with anti-CD98 antibodies could be beneficial for the treatment of AML in both adults and children,” Dr Reya said.
Moving forward, Dr Reya and her colleagues are working to further define whether CD98 could be used to treat pediatric AML.
“Many of the models we used in this work were based on mutations found in childhood AML,” Dr Reya said. “While many childhood cancers have become very treatable, childhood AML continues to have a high rate of relapse and death.”
“We plan to work with pediatric oncologists to test if anti-CD98 agents can be effective against pediatric AML and whether it can improve responses to current treatments. I think this is particularly important to pursue since the anti-CD98 antibody has already been through phase 1 trials and could be more easily positioned to test in drug-resistant pediatric AML.”
Igenica Biotherapeutics Inc., the company developing IGN523, provided the drug for this study, and one of the study’s authors is an employee of the company.