Editor’s note: Find the latest COVID-19 news and guidance in Medscape’s Coronavirus Resource Center.
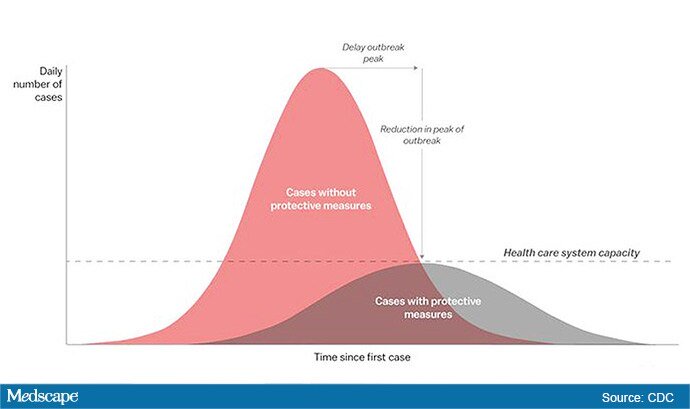
The “Flattening the Curve” graphic, which has, to not use the term lightly, gone viral on social media, visually explains the best currently available strategy to stop the COVID-19 spread, experts told Medscape Medical News.
The height of the curve is the number of potential cases in the United States; along the horizontal X axis, or the breadth, is the amount of time. The line across the middle represents the point at which too many cases in too short a time overwhelm the healthcare system.
Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham’s School of Medicine explained.
“Not only are you spreading out the new cases but the rate at which people recover,” she told Medscape Medical News. “You have time to get people out of the hospital so you can get new people in and clear out those beds.”
The strategy, with its own Twitter hashtag, #Flattenthecurve, “is about all we have,” without a vaccine, Marrazzo said.
Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said avoiding spikes in cases could mean fewer deaths.
“If you look at the curves of outbreaks, you know, they go big peaks, and then they come down. What we need to do is flatten that down,” Fauci said March 10 in a White House briefing. “You do that by trying to interfere with the natural flow of the outbreak.”
Wuhan, China, at the epicenter of the pandemic, “had an explosive curve” and quickly got overwhelmed without early containment measures, Marrazzo noted. “If you look at Italy right now, it’s clearly in the same situation.”
The Race Is On to Interrupt the Spread
The race is on in the US to interrupt the transmission of the virus and slow the spread, meaning containment measures have increasingly higher and wider stakes.
Closing down Broadway shows and some theme parks and massive sporting events; the escalating numbers of people working from home; and businesses cutting hours or closing all demonstrate the level of US confidence that “social distancing” will work, Marrazzo said.
“We’re clearly ready to disrupt the economy and social infrastructure,” she said.
That appears to have made a difference in Wuhan, Marrazzo said, as the new infections are coming down.
The question, she said, is “we’re not China – so are Americans really going to take to this? Americans greatly value their liberty and there’s some skepticism about public health and its directives. People have never seen a pandemic like this before.”
Dena Grayson, MD, PhD, a Florida-based expert in Ebola and other pandemic threats, told Medscape Medical News that EvergreenHealth in Kirkland, Washington, is a good example of what it means when a virus overwhelms healthcare operations.
The New York Times reported that supplies were so strained at the facility that staff were using sanitary napkins to pad protective helmets.
As of March 11, 65 people who had come into the hospital have tested positive for the virus, and 15 of them had died.
Grayson points out that the COVID-19 cases come on top of a severe flu season and the usual cases hospitals see, so the bar on the graphic is even lower than it usually would be.
“We have a relatively limited capacity with ICU beds to begin with,” she said.
So far, closures, postponements, and cancellations are woefully inadequate, Grayson said.
“We can’t stop this virus. We can hope to contain it and slow down the rate of infection,” she said.
“We need to right now shut down all the schools, preschools, and universities,” Grayson said. “We need to look at shutting down public transportation. We need people to stay home – and not for a day but for a couple of weeks.”
The graphic was developed by visual-data journalist Rosamund Pearce, based on a graphic that had appeared in a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) article titled “Community Mitigation Guidelines to Prevent Pandemic Influenza,” the Times reports.
Marrazzo and Grayson have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com .