In light of the rapid changes affecting cancer clinics due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. David Kerr and Dr. Rachel Kerr, both specialists in gastrointestinal cancers at the University of Oxford in Oxford, United Kingdom, drafted these guidelines for the use of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Dr. Kerr and Dr. Kerr are putting forth this guidance as a topic for discussion and debate.
Our aim in developing these recommendations for the care of colorectal cancer patients in areas affected by the COVID-19 outbreak is to reduce the comorbidity of chemotherapy and decrease the risk of patients dying from COVID-19, weighed against the potential benefits of receiving chemotherapy. These recommendations are also designed to reduce the burden on chemotherapy units during a time of great pressure.
We have modified the guidelines in such a way that, we believe, will decrease the total number of patients receiving chemotherapy – particularly in the adjuvant setting – and reduce the overall immune impact of chemotherapy on these patients. Specifically, we suggest changing doublet chemotherapy to single-agent chemotherapy for some groups; changing to combinations involving capecitabine rather than bolus and infusional 5-FU for other patients; and, finally, making reasonable dose reductions upfront to reduce the risk for cycle 1 complications.
By changing from push-and-pump 5-FU to capecitabine for the vast majority of patients, we will both reduce the rates of neutropenia and decrease throughput in chemotherapy outpatient units, reducing requirements for weekly line flushing, pump disconnections, and other routine maintenance.
We continue to recommend the use of ToxNav germline genetic testing as a genetic screen for DPYD/ENOSF1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify patients at high risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity.
Use of biomarkers to sharpen prognosis should also be considered to refine therapeutic decisions.
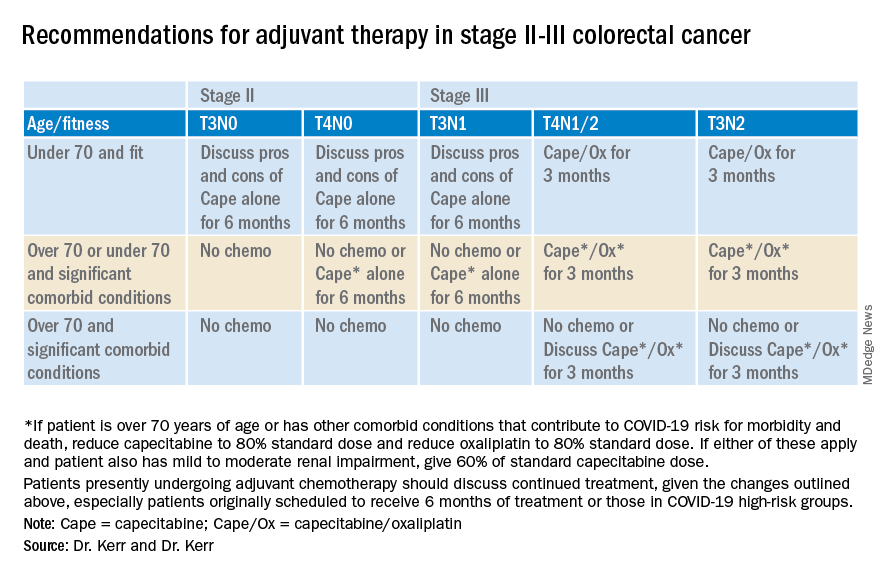
Recommendations for stage II-III colorectal cancer
Recommendations for advanced colorectal cancer
Which regimen? Capecitabine/oxaliplatin should be the default backbone chemotherapy (rather than FOLFOX) in order to decrease the stress on infusion units.
Capecitabine plus irinotecan should be considered rather than FOLFIRI. However, in order to increase safety, reduce the dose of the capecitabine and the irinotecan, both to 80%, in all patient groups; and perhaps reduce the capecitabine dose further to 60% in those over the age of 70 or with significant comorbid conditions.
Treatment breaks. Full treatment breaks should be considered after 3 months of treatment in most patients with lower-volume, more indolent disease.
Treatment deintensification to capecitabine alone should be used in those with higher-volume disease (for example, more than 50% of liver replaced by tumor) at the beginning of treatment.
Deferring the start of any chemotherapy. Some older patients, or those with significant other comorbidities (that is, those who will be at increased risk for COVID-19 complications and death); who have low-volume disease, such as a couple of small lung metastases or a single liver metastasis; or who were diagnosed more than 12 months since adjuvant chemotherapy may decide to defer any chemotherapy for a period of time.
In these cases, we suggest rescanning at 3 months and discussing further treatment at that point. Some of these patients will be eligible for other interventions, such as resection, ablation, or stereotactic body radiation therapy. However, it will be important to consider the pressures on these other services during this unprecedented time.
Chemotherapy after resection of metastases. Given the lack of evidence and the present extenuating circumstances, we would not recommend any chemotherapy in this setting.
David J. Kerr, MD, CBE, MD, DSc, is a professor of cancer medicine at the University of Oxford. He is recognized internationally for his work in the research and treatment of colorectal cancer, and has founded three university spin-out companies: COBRA Therapeutics, Celleron Therapeutics, and Oxford Cancer Biomarkers. In 2002, he was appointed Commander of the British Empire by Queen Elizabeth. Rachel S. Kerr, MBChB, is a medical oncologist and associate professor of gastrointestinal oncology at the University of Oxford. She holds a UK Department of Health Fellowship, where she is clinical director of phase 3 trials in the oncology clinical trials office.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.