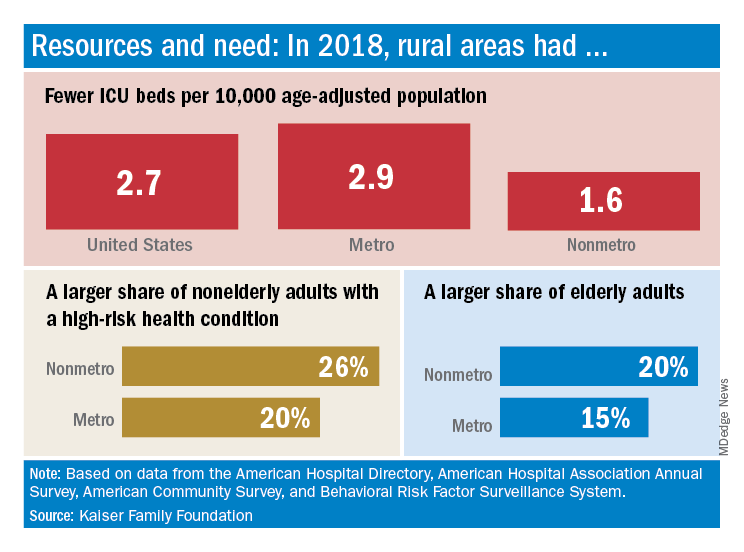
The nonmetropolitan, largely rural, areas of the United States have fewer ICU beds than do urban areas, but their populations may be at higher risk for COVID-19 complications, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
In 2018, the United States had 2.7 ICU beds per 10,000 age-adjusted population, but that number drops to 1.6 beds per 10,000 in nonmetro America and rises to 2.9 per 10,000 in metro areas. Counts for all hospital beds were much closer: 21.6 per 10,000 (rural) and 23.9 per 10,000 (urban), Kaiser investigators reported.
“The novel coronavirus was slower to spread to rural areas in the U.S., but that appears to be changing, with new outbreaks becoming evident in less densely populated parts of the country,” Kendal Orgera and associates said in a recent analysis.
Those rural areas have COVID-19 issues beyond ICU bed counts. Populations in nonmetro areas are less healthy – 26% of adults under age 65 years had a preexisting medical condition in 2018, compared with 20% in metro areas – and older – 20% of people are 65 and older, versus 15% in metro areas, they said.
“If coronavirus continues to spread in rural communities across the U.S., it is possible many [nonmetro] areas will face shortages of ICU beds with limited options to adapt. Patients in rural areas experiencing more severe illnesses may be transferred to hospitals with greater capacity, but if nearby urban areas are also overwhelmed, transfer may not be an option,” Ms. Orgera and associates wrote.
They defined nonmetro counties as those with rural towns of fewer than 2,500 people and/or “urban areas with populations ranging from 2,500 to 49,999 that are not part of larger labor market areas.” The Kaiser analysis involved 2018 data from the American Hospital Association, American Hospital Directory, American Community Survey, and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.