COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
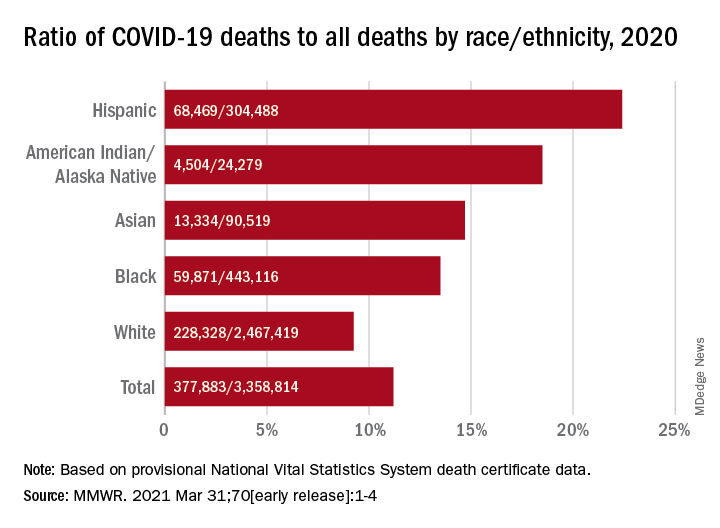
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”