SAN FRANCISCO – Victims of elder abuse who have perceived strong social support from family or friends are “completely inoculated” against the otherwise dramatically increased risk of trauma-related psychopathology that pertains to mistreated seniors who lack such support, according to Ron Acierno, PhD.
Dr. Acierno, professor of nursing at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston, presented 8-year follow-up data from the National Elder Mistreatment Study, the largest study of elder abuse ever conducted in the United States.
“Importantly, high social support virtually eliminated the risk of psychopathology and poor health associated with mistreatment. Thus, when social support from family or friends is unavailable or deficient, policy should direct services to compensate or supplement this factor,” he said at the annual conference of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America. .The National Elder Mistreatment Study involved 5,777 randomly selected community-dwelling older adults who, in 2008, participated in structured interviews assessing whether they had experienced physical, psychological, sexual, or neglectful mistreatment. The study made headlines by documenting an unexpectedly high 11% rate of elder mistreatment within the previous 12 months (Am J Public Health. 2010 Feb;100[2]:292-7).
Eight years later, Dr. Acierno and his coinvestigators were able to recontact 173 of the original 684 abused elders, as well as 602 nonabused controls for structured interviews assessing their current mental health. At that point, the participants averaged 84.9 years of age.
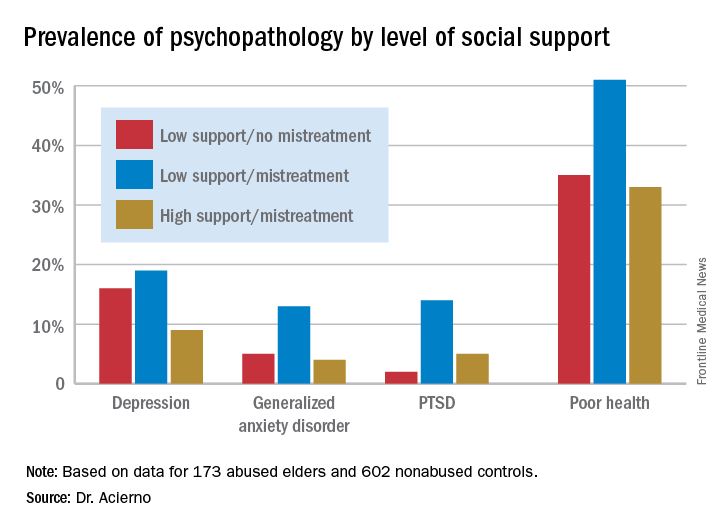
Striking differences in mental health status based on elder abuse history were documented. The prevalences of depression, generalized anxiety disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder were 13%, 7%, and 8%, respectively, in the elder abuse group, compared with 5%, 1%, and 1% in the nonabused controls. Of the group subjected to abuse 8 years earlier, 40% were categorized at follow-up as “in poor health,” compared with 23% of controls.
More importantly, high social support essentially erased the elder abuse group’s increased risk (see graphic), Dr. Acierno said.
The National Elder Mistreatment Study was funded by the National Institute of Justice, the National Institute on Aging, and the Archstone Foundation. Dr. Acierno reported having no financial conflicts.