according to a new survey by Health Union, a family of online health communities.
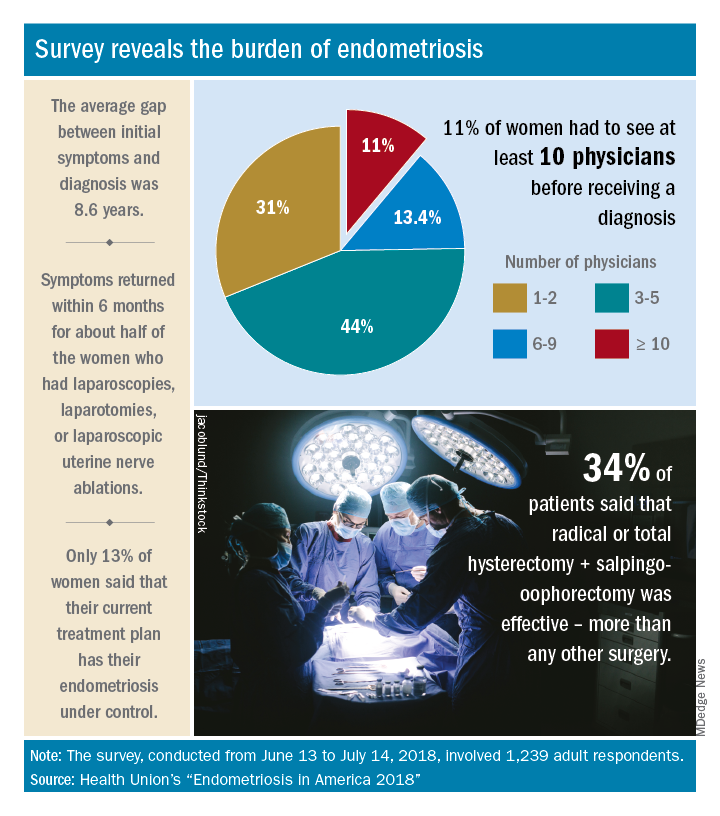
Advances in support and understanding have been made through research and dissemination of information via the Internet, but complete control of endometriosis remains elusive, as only 13% of the 1,239 women surveyed from June 13 to July 14, 2018, said that their condition was under control with their current treatment plan.
Before control, of course, comes diagnosis, and the average gap between onset of symptoms and diagnosis was 8.6 years. Such a gap “can lead to delayed treatment and a potentially negative impact on quality of life,” Health Union said in a written statement. Those years of delays often involved visits to multiple physicians: 44% of respondents saw 3-5 physicians before receiving a diagnosis and 11% had to see 10 or more physicians.
“When comparing differences between symptom onset-to-diagnosis groups, there are some significant findings that suggest a fair amount of progress has been made, for the better,” Health Union said, noting that women who received a diagnosis in less than 5 years “were significantly less likely to think their symptoms were related to their menstrual cycles than those with a longer symptoms-to-diagnosis gap.” Respondents who had a gap of less than 2 years “were more likely to seek medical care as soon as possible” and to have used hormone therapies than those with longer gaps, the group said.
The most common diagnostic tests were laparoscopy, reported by 85% of respondents, and pelvic/transvaginal ultrasound, reported by 46%. Of the women who did not have a laparoscopy, 43% were undergoing a surgical procedure for another condition when their endometriosis was discovered. Laparoscopy also was by far the most common surgery to treat endometriosis, with a 79% prevalence among respondents, compared with 16% for laparotomy and 12% for oophorectomy, Health Union reported in Endometriosis in America 2018.
Common nonsurgical tactics to improve symptoms included increased water intake (79%), use of a heating pad (75%), and increased fresh fruit (64%) or green vegetables (62%) in the diet. Three-quarters of respondents also tried alternative and complementary therapies such as vitamins, exercise, and acupuncture, the report showed.
“Living with endometriosis is much easier now than it was not even a decade ago, as the Internet and social media have definitely increased knowledge about the disease,” said Endometriosis.net (one of the Health Union online communities) patient advocate Laura Kiesel. “When I first suspected I had the disease, in the mid-90s, hardly anyone had heard about it, and those aware of it didn’t think it was very serious. All these years later, I get a lot more sympathy and support – both online and in person – and people understand how serious, painful, and life altering it could be.”