CHICAGO– Visceral obesity was associated with low bone mineral density in a study of premenopausal women, indicating that abdominal fat is a risk factor for osteoporosis.
The finding indicates that "obesity does not always protect against osteoporosis," study investigator Dr. Miriam A. Bredella said in a press briefing at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America. "Excessive visceral fat is not only a risk factor for heart disease and diabetes, but also for bone loss."
The study flies in the face of current thinking that obesity actually protects against osteoporosis. Previous studies suggesting a link between fat and bone health focused primarily on body mass index (BMI), which incorporates measures of muscle and bone mass and subcutaneous fat as well as visceral fat, she said. The present study zeroed in specifically on visceral fat.
Dr. Bredella noted "disturbing pictures emerging from the obesity epidemic, because the number of forearm fractures among young patients has increased dramatically over the last year, and the strongest risk factor in that group ... was actually increased body weight." This finding prompted the investigators to see whether there was a connection between osteoporosis and fat, said Dr. Bredella of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston
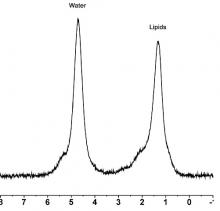
In the present study, 50 premenopausal women with a BMI of 19-46 kg/m2 (mean 30) underwent a magnetic resonance spectroscopy exam to assess L4 bone marrow (BM) fat, followed by quantitative computed tomography to assess trabecular bone mineral density (BMD).
The results showed a positive correlation between visceral fat and BM fat (r = 0.28) and an inverse association between visceral fat and BMD (r = –0.31) and between vertebral BM fat and BMD (r = –0.45). These results were statistically significant. There was no correlation between either subcutaneous fat (fat concentrated around the hips and thighs) or total body fat and either BM fat or BMD.
These results reveal the distinctly detrimental effect of abdominal obesity on bone health, Dr. Bredella said.
The study is among the first to explore the relationship between body fat and bone marrow fat, and the dynamic appears to be complex, she said in an interview. According to recent research, "the amount of fat within your bones could predict if you will develop a fracture independent of bone mineral density," she noted. A recent study by Dr. Bredella and her colleagues found that women with anorexia nervosa had three times the amount of bone marrow fat as did normal-weight women.
Dr. Bredella had no financial disclosures.