Suicide rates in young people aged 10-24 years increased significantly in 42 states from 2007-2009 to 2016-2018, according to a recent analysis from the National Center for Health Statistics.
Nationally, the suicide rate jumped 47%, based on the averages for the two 3-year periods, rising from 7.0 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years to 10.3 per 100,000. For all ages, the corresponding increase was 47%, Sally C. Curtin, MA, of the NCHS, said in a National Vital Statistics Report.
There was no state with a decrease in suicide rates for adolescents and young adults, as the other eight all had nonsignificant increases, the smallest being 14% in South Dakota. Three-year averages were used to increase statistical power for states with relatively small numbers of deaths but were still not enough to show significance for some large increases, such as the 48% rise in Delaware, Ms. Curtin noted.
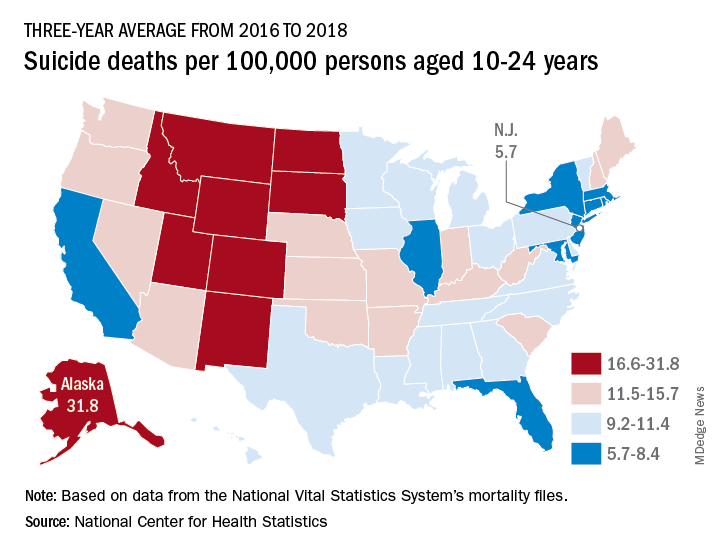
In 2016-2018, Alaska’s suicide rate of 31.8 per 100,000 persons aged 10-24 years was the highest in the country, followed by South Dakota (23.6), Montana (23.2), and Wyoming (20.5). New Jersey had the lowest rate at 5.7 per 100,000, with New York and Rhode Island both slightly higher at 5.9 and Connecticut at 6.3, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Even the low numbers, however, hide some large changes, as New Jersey (up by 39%) and New York (up by 44%) were among the 42 states with statistically significant increases, which ranged from 21.7% in Maryland to 110% in New Hampshire, Ms. Curtin said in the report. The increases seen in this analysis contrast with data from the preceding time period, as “the suicide rate among persons aged 10-24 was statistically stable from 2000 to 2007.”
SOURCE: Curtin SC. National Vital Statistics Reports. 2020;69(11)1-9.