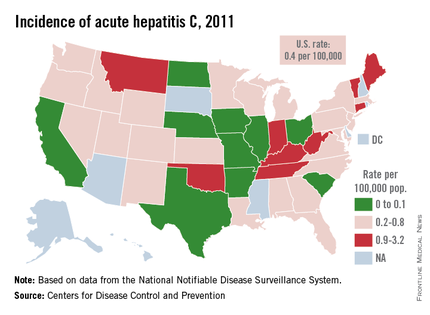
Kentucky has the highest rate of acute hepatitis C infection – 3.2 cases per 100,000 population – in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Based on reports from 2011, the last year for which data are available, there were 142 cases of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in Kentucky, which was 58 more than Indiana, the state with the second-highest number of cases, and 96 more than West Virginia, the state with the second-highest rate, the CDC reported.
Among the 42 states that submitted reports to the CDC’s National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System, the average rate of acute HCV infection was 0.4 cases per 100,000. The U.S. total of 1,229 cases represents a 44% increase over 2010. Three states – Arkansas, Iowa, and North Dakota – reported zero cases for 2011, the report said.
The CDC also noted that most cases of hepatitis are not reported, and after adjusting for asymptomatic infections and underreporting, the agency estimated that 16,500 new HCV infections occurred in 2011.