Adult women with no regular health care provider or no health insurance were much less likely to have been screened for cervical cancer in the past 5 years, a study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed.
In 2012, an estimated 11.4% of U.S. women aged 21-65 years had not had a Pap test to screen for cervical cancer in the past 5 years, compared with 25.5% of women without a regular health care provider and 23.1% of those without insurance, the CDC reported (MMWR 2014;63:1004-9).
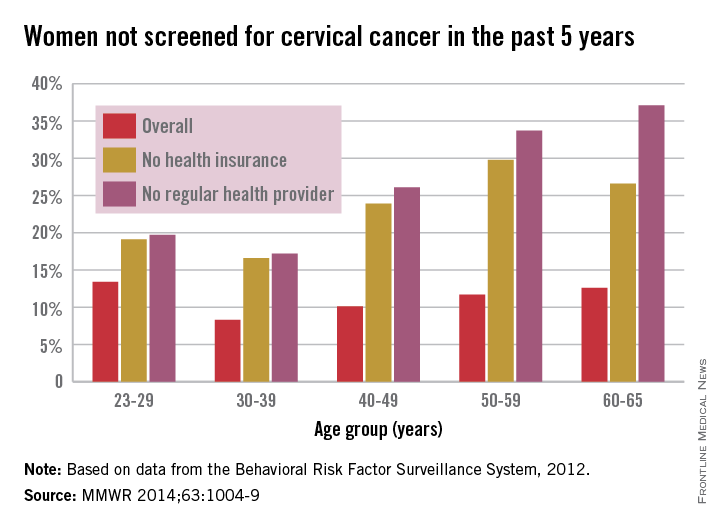
By age group, women aged 30-39 years had the lowest overall rate, with only 8.3% not receiving screening in the past 5 years, as well as the lowest rates for those who did not have health insurance or a health care provider, at 16.6% and 17.2%, respectively. In 2012, women aged 23-29 years had the highest overall rate at 13.4%, women aged 50-59 years had the highest rate for no insurance at 29.8%, and women aged 60-65 years had the highest rate for no health care provider at 37.1%.
By ethnicity, black women had the lowest overall 5-year nonscreening rate at 9.2%, although Hispanics had the lowest rate for women without health insurance or a health care provider, at 16.7% and 18.4%, respectively. At 19.7%, Asian/Pacific Islanders had the highest overall rate, as well as the highest rate for women without health insurance at 32.5% and women without a regular health care provider at 40.8%, according to data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
From 2007 to 2011, a total of 62,150 cervical cancer cases were reported in the United States, and in 2011, the incidence rate was 7.5 per 100,000 people, with the rate falling an average of 1.9% a year over that 5-year period. For the same time period, there were 19,969 deaths, with the overall U.S. death rate at 2.3 per 100,000 people in 2011, with a slight average decrease per year but not enough to be statistically significant, the CDC noted.