While independent registries have been shown to be effective in improving care [13,14,23], they involve extra time and effort for data entry, can be difficult and expensive to maintain, and may not be feasible for many systems that care for SCD patients. In this paper, we describe the development and use of our EHR-based SCD registry for children with SCD, including our efforts to engage key technical and clinical experts to develop an EHR that is tailored to the outpatient workflow and data collection of quality measures and implement a fully functional system that collects data on quality measures to support case management and continuous QI.
Methods
This study was conducted at Boston Medical Center, New England’s largest safety net hospital, which cares for 190 children with SCD ages 0 to 21 years. The outpatient EHR (Centricity, GE) has been in use since 2000 and is used for all aspects of outpatient care, including ordering of immunizations and tests, electronic prescription writing, and referrals to specialty care.
Outcome Measures
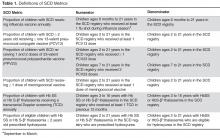
Based on the literature [3–5,7,24], national guidelines [25], and published quality indicators [16], we focused on care processes shown to decrease morbidity and mortality in pediatric SCD: receipt of influenza, pneumococcal, and meningococcal vaccines, (2) transcranial Doppler screening, and (3) hydroxyurea therapy ( Table 1 ).Vaccines: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends vaccinating children with SCD [26] against influenza annually, given their susceptibility to the influenza virus [24,27]. The CDC also recommends the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23 2-dose series) and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13, per childhood routine vaccine schedule for young children and 1 catch-up dose for children previously vaccinated with PCV7), and meningococcal vaccine (2-dose series), given patients’ functional asplenic status [25,28].
Transcranial Doppler screening can identify children with hemoglobin (Hb) SS and Hb S-β 0 thalassemia at higher risk of stroke, which may be prevented through hypertransfusion programs [4]. Screening is recommended annually for these children ages 2 to 16 years [25].
Hydroxyurea use among children with Hb SS and Hb S-β 0 thalassemia is an established practice [29,30]. We consider hydroxyurea therapy for all children 2 years and older with Hb SS and Hb S-β 0 thalassemia, given the recently published safety data from the Baby-HUG trial [7] and the benefits of hydroxyurea among children and adults with SCD [6,31–35].
EHR-based Registry
Our EHR-based SCD registry includes 3 key components: (1) forms to support detailed documentation at the point-of-care (ie, clinic visit); (2) a registry management form to allow the QI team to identify patients to be included or excluded from the registry; and (3) a central data warehouse to support quality measurement and improvement.
Documentation in the EHR is performed using a set of customized templates or “forms.” These forms allow documentation of care provision in a structured way. The discrete data elements are stored within the data warehousing system that supports the EHR. The SCD forms used in this project were a revised version of existing forms used by our pediatric hematologists for the past 6 years. The primary goal was to improve efficiency in a patient encounter and enhance data collection efforts. In particular, several changes were made to enhance data collection for quality measures included in the SCD registry. First, we collected genotype in a standardized way to better define subpopulations of SCD patients, as some of the care provided is dictated by genotype. We also expanded data capture for transcranial Doppler screening to include date of last screening to prompt scheduling. For hydroxyurea, the forms now capture if hydroxyurea has been prescribed, and if not, why (eg, declined, not indicated); adherence, current dose, and routine labs for monitoring are also listed to aid in clinical decision-making. Finally, the forms were revised to prominently display the subset of immunizations important to SCD (described above) to assess if the patient is current.