The annual number of new HIV infections has remained stable in recent years, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that’s not good – but solutions are at hand.
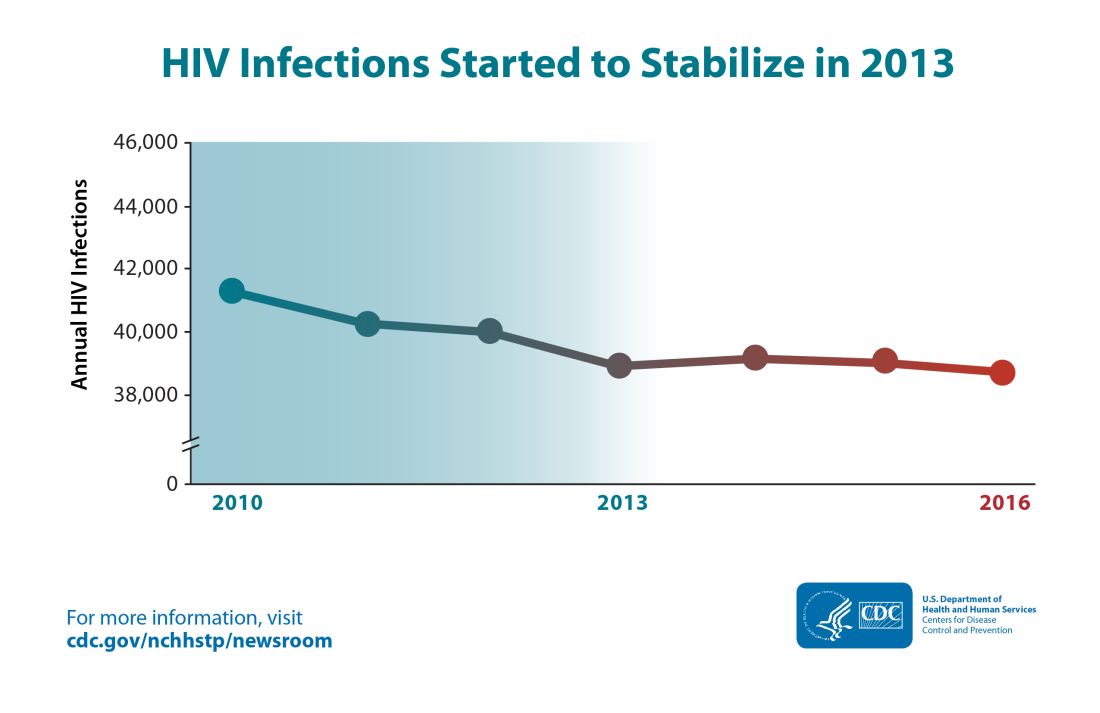
“Progress in HIV prevention has stalled,” according to a fact sheet accompanying a new CDC report detailing HIV infection data in the United States from 2010 to 2016.Though the estimated number of new HIV infections declined from just under 42,000 per year in 2010 to about 39,000 annually in 2013, that figure was essentially unchanged by 2016, with 38,700 new HIV infections seen that year.
“CDC estimates that the decline in HIV infections has plateaued because effective HIV prevention and treatment are not adequately reaching those who could most benefit from them. These gaps remain particularly troublesome in rural areas and in the South and among disproportionately affected populations like African Americans and Latinos,” said the CDC in a press release accompanying the report.
The report comes soon after President Trump’s State of the Union address, which announced a new multiagency initiative to eliminate the HIV epidemic in the United States, with the goal of reducing new HIV infections by 90% over the next 10 years. The multipronged initiative will implement geographically targeted HIV elimination teams in areas with high HIV prevalence, pulling together federal agencies, local and state governments, and community-level resources.
The initiative, called “Ending the Epidemic: A Plan for America” will combine an intensified approach to early diagnosis and treatment with efforts to boost uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis for individuals at high risk for HIV infection.
The new CDC report used CD4 counts reported to the National HIV Surveillance System at the time of diagnosis to identify new (incident) cases and to track prevalence. Much of the report is devoted to finely detailed reporting of HIV incidence across sex, age, race/ethnicity, and transmission mode.
Though some groups, such as people who inject drugs, have seen a decrease of about 30% in the annual rate of new HIV cases, new cases have jumped for other groups. In particular, Latino gay and bisexual men saw new cases climb from 6,400 per year in 2010 to 8,300 in 2016. The incidence rate has stayed high and stable among African American gay and bisexual men, with 9,800 new cases reported in 2010; the same number was seen in 2016.
Among gay and bisexual men overall, the rate has also stayed stable, with about 26,000 new HIV infections reported at the beginning and end of the studied period. White heterosexual women saw about 1,000 new cases per year in 2010 and in 2016.
Some groups saw declines in new cases: African American and Latina heterosexual women each saw a falling incidence of new HIV cases. For the former group, new cases fell from 4,700 to 4,000, while the latter group of women saw new cases drop from 1,200 to 980 per year from 2010 to 2016.
Within these broad groups, HIV incidence also rose among some age groups and fell among others. Decreases were seen for younger African American gay and bisexual men (those aged 13-24 years), but rates increased by about two-thirds for men in this group aged 25-34 years. A similar increase was seen for Latino men in the 25-34 years age group, a change which drove the overall 30% increase in new infections for Latino gay and bisexual men.
White gay and bisexual men saw across-the-board decreases in new infections, though the overall decrease was less than 20%.
For heterosexual individuals as a group, new infections dropped by about 17%, from 10,900 to 9,100 annually. This change was driven mostly by decreases in women identifying as heterosexual.
“After a decades-long struggle, the path to eliminate America’s HIV epidemic is clear,” said Eugene McCray, MD, director of CDC’s Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention, in the press release. “Expanding efforts across the country will close gaps, overcome threats, and turn around troublesome trends.”
The press release cited local work in Washington and New York as evidence that targeted resources can make a difference in reducing new HIV cases. In these two areas, new infections dropped by 23% and 40% respectively from 2010 to 2016.
SOURCE: Centers for Disease Control. CDC Report: www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance.html.