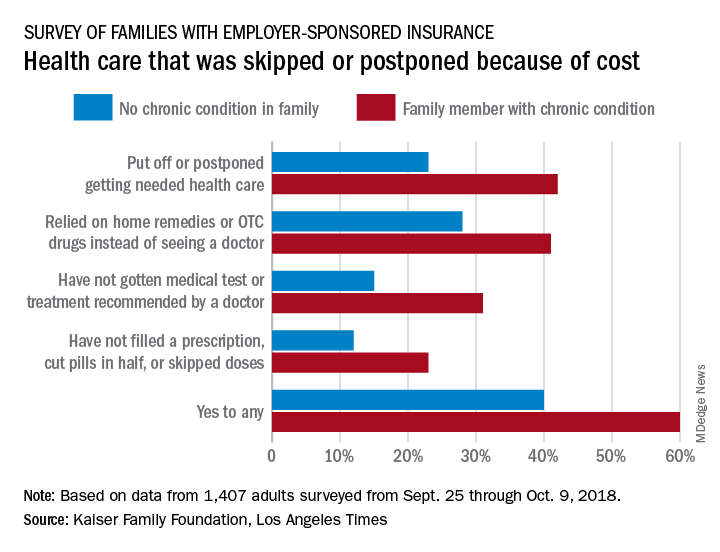
Half of all Americans with employer-sponsored health benefits say that they or someone in their family has skipped or postponed care because of the cost, according to a survey by the Kaiser Family Foundation and the Los Angeles Times.
That number changes, however, when chronic conditions are considered. In the survey of Americans covered by employer-sponsored health insurance, 60% of those with a family member who had a chronic condition said that cost had altered the care of someone in the family over the previous 12 months, compared with 40% of those who had no chronic condition in their family, the KFF and L.A. Times noted in their report.
More specifically, families with an individual who had a chronic condition were more likely to put off or postpone needed care (42% vs. 23%) and to rely on home remedies or OTC drugs instead of visiting a physician (41% vs. 28%) than were families without chronic conditions, the report’s authors said.
When asked about the affordability of their health care, 49% of those in families with a chronic health condition said they had a problem paying for their coverage in the past year, compared with 29% of respondents in families with no chronic condition.
“Drilling down into the consequences of these affordability problems reveals more about the financial burden of health care on families with chronic conditions,” compared with those without chronic conditions: cut back spending on food, clothes, household items (35% vs. 16%); used up all or most of their savings (26% vs. 11%); and borrowed money from friends or family (14% vs. 6%), according to the researchers.
Although respondents felt “that the cost of health care for people like them is too high, more say the current U.S. health insurance system works well for people with employer coverage than say it works well for people on Medicare or Medicaid or those who purchase their own insurance. Asked who is to blame for high costs, majorities point the finger at pharmaceutical and insurance companies, while fewer see hospitals, doctors, or employers as deserving of blame,” the KFF and L.A. Times investigators wrote.
The survey involved a sample of 1,407 adults aged 18-64 years and was conducted from Sept. 25 through Oct. 9, 2018. The margin of the sampling error is ±3 percentage points.