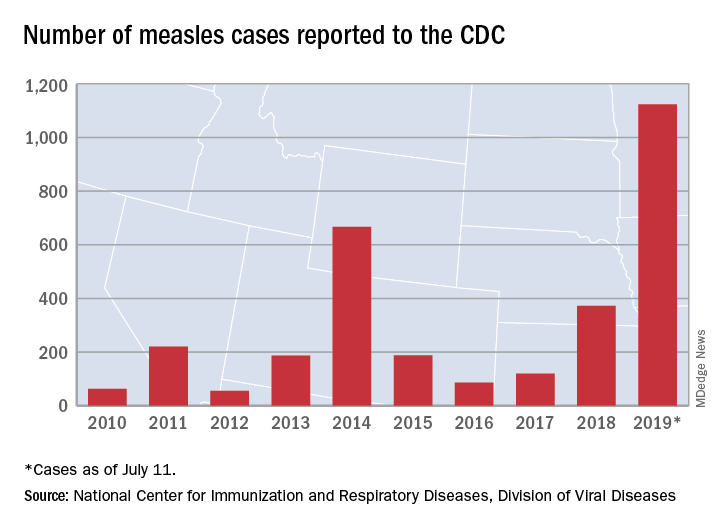
The United States continues to slowly add new cases of measles to 2019’s postelimination-record total, but California was officially removed from the outbreak list this week, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That is the highest number of cases reported since measles was declared eliminated in 2000 and the most in a single year since 1992.
The end of outbreak-related activity in California leaves three locations still dealing with ongoing cases: Rockland County, N.Y.; New York City; and King, Pierce, and Snohomish Counties in Washington, the CDC said.
Those three jurisdictions currently report the following:
- reported four new cases from July 3 to July 11 and is up to 175 cases for the year.
- had one new case from July 1 to July 8 and is now at 564 for the year.
- reported two cases from July 1 to July 10 and is now at 10 for the year (the other two counties have a total of three cases). Clark County in Washington reported 71 cases in an earlier, unrelated outbreak.