Results
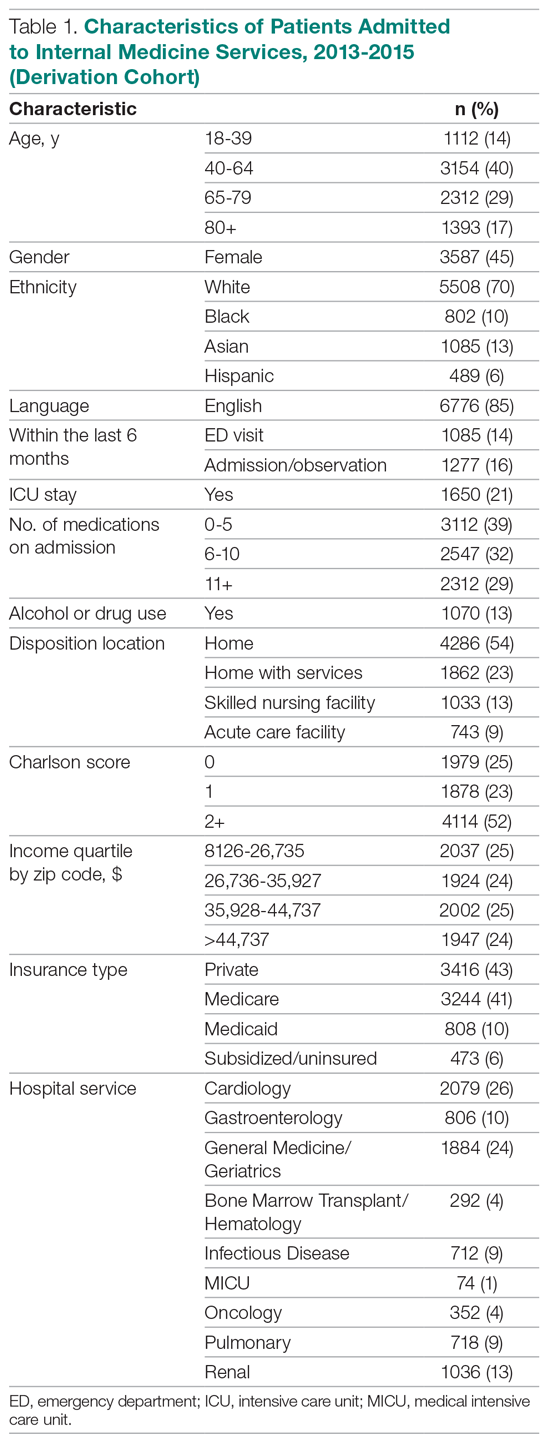
The derivation cohort consisted of 7972 index admissions, of which 12.6% were readmitted within 30 days. The patient population was 45% female, 70% white, and 85% English-speaking, with an average age of 61.4 years (standard deviation, 18.1, Table 1). Most patients had either private insurance (43%) or Medicare (41%).
Many patients were medically complex: 21% required ICU care, 29% were taking 11 or more medications on admission, and 52% had a Charlson score of 2 or more. In the previous 6 months, 14% had an emergency department visit and 16% had an admission or overnight observation. The rate of drug or alcohol abuse was 13%. The majority of patients were discharged home without services (54%), while 23% were discharged home with services, 13% were discharged to a skilled nursing facility, and 9% were discharged to an acute care facility.
Factors Associated With 30-Day Readmission
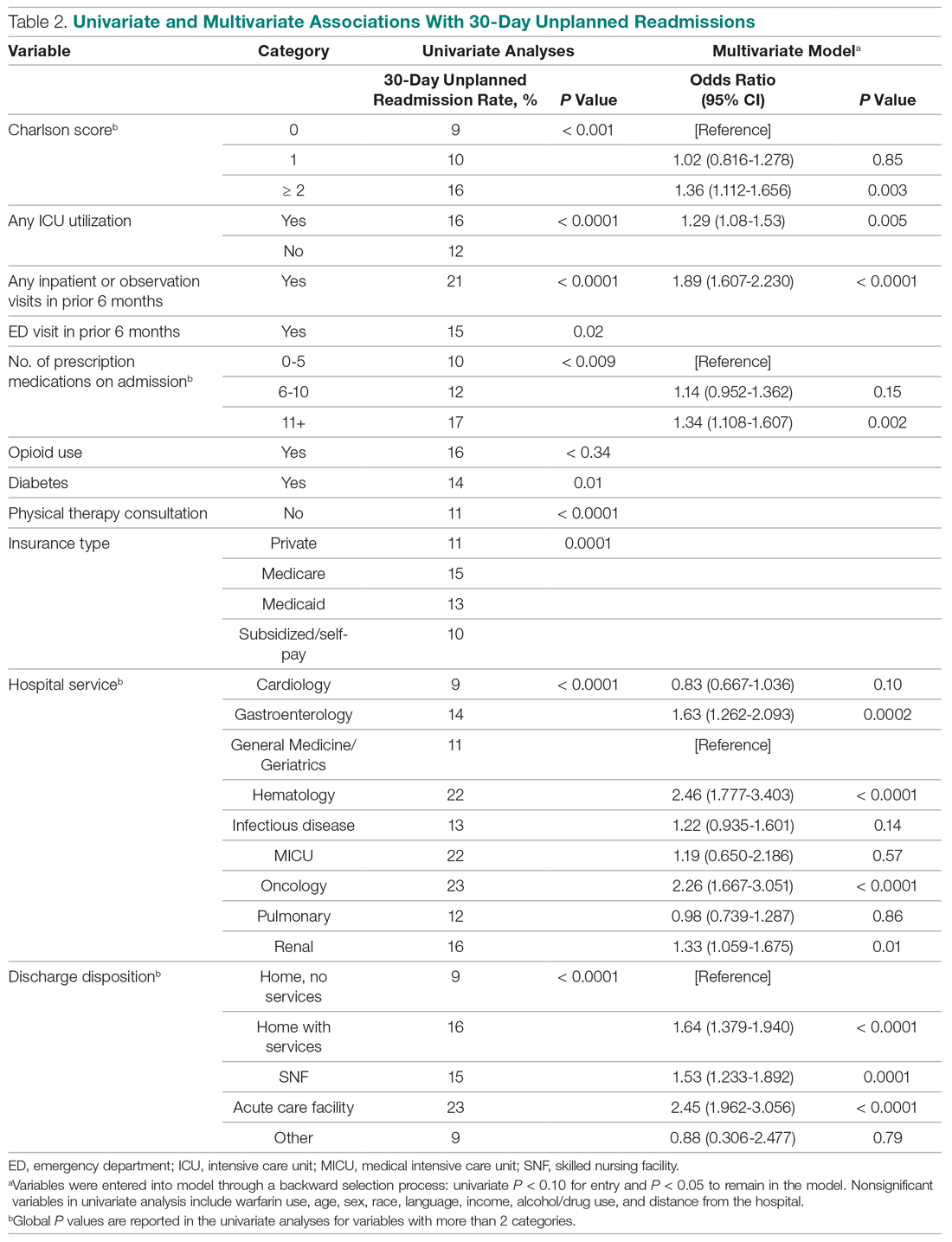
Table 2 displays the univariate and multivariate associations with 30-day readmissions in the derivation cohort. Variables significantly associated with readmission in univariate analysis were Charlson comorbidity score, history of diabetes, ICU utilization, previous emergency department visit, inpatient or observation stay within 6 months, number of medications on admission, use of opioids on admission, a diagnosis of diabetes, type of insurance, physical therapy consultation, admitting service, and discharge disposition. Variables not significant in univariate analysis included warfarin use, alcohol/drug abuse, distance from the hospital, and demographic variables (age, sex, race, language, income by zip code).
Variables associated with readmission in the final multivariate analysis model included a Charlson score of 2 or higher (compared to a score of 0; odds ratio [OR], 1.36; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.11-1.66); any ICU stay (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.08-1.53); number of medications on admission (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.11-1.61) for 11 or more compared with 5 or fewer medications; prior admission or overnight observation (OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.61-2.23); and disposition on discharge to an acute care facility (OR, 2.45; 95% CI, 1.96-3.06), skilled nursing facility (OR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.23-1.89), or home with services (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.38-1.94) compared with home discharge without services. The hospital service from which the patient was discharged was significantly associated with readmission; the subspecialty services with the highest odds ratios were bone marrow transplant/hematology (OR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.77-3.40) and oncology (OR, 2.26; 95% CI, 1.67-3.05), as compared with general medicine/geriatrics.