When it comes to COVID-19, studies show that social distancing flattened the curve.
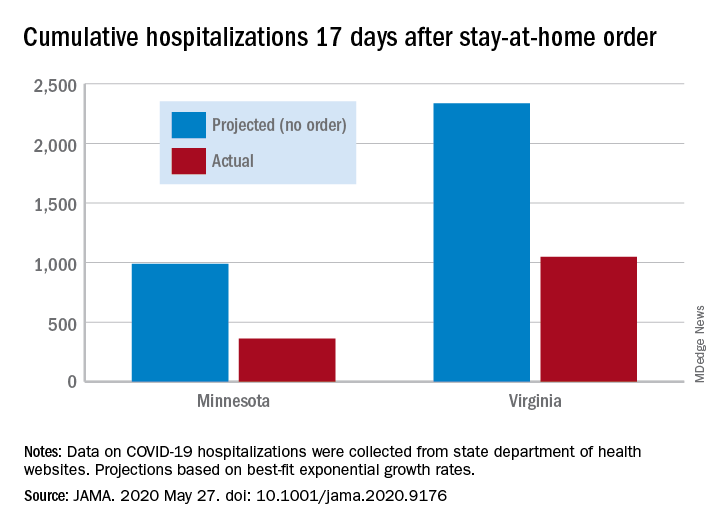
Cumulative hospitalizations in four states with stay-at-home orders were well short of the projected exponential growth curves, Soumya Sen, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and associates reported May 27 in a research letter in JAMA. All states were observed through April 28.
The deviations between observed cases and worst-case projections in the four states – Colorado, Minnesota, Ohio, and Virginia – all began within 8-10 days of the stay-at-home orders. In Minnesota, 17 days after the order, there were 361 cumulative hospitalizations, compared with a projection of 988 had no such action been taken. In Virginia, the corresponding numbers were 1,048 observed and 2,335 projected, they reported.
“Observed hospitalizations consistently fell outside of the 95% prediction bands of the projected exponential growth curve,” Dr. Sen and associates noted.
In a separate Canadian study measuring COVID-19 patients occupying ICU beds in Ontario and deaths among those cases, hospitals “would have rapidly exceeded ICU capacity and observed substantially higher mortality” without any physical distancing intervention, Ashleigh R. Tuite, PhD, MPH, of the University of Toronto and associates wrote May 27 in a letter in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Their model, based on a 70% reduction in physical contacts for March 19–May 3, projected 2.0 cases per 100,000 population with physical distancing and 37.4 per 100,000 without. Deaths among those ICU patients were projected at 2.5 per 100,000 with distancing and 12.7 per 100,000 without intervention, they reported.
“Our modeling also shows the challenges associated with relaxation of physical distancing measures without a concomitant increase in other public health measures. Specifically, when the number of contacts between persons returns to more than 50% of normal, we expect disease activity to resurge rapidly and ICUs to quickly reach capacity,” they wrote.
The study published in JAMA used publicly available data from the University of Minnesota COVID-19 Hospitalization Project, which is partially funded by the University of Minnesota Office of Academic Clinical Affairs and United Health Foundation.
SOURCES: Sen S et al. JAMA. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9176; Tuite AR et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 27. doi: 10.7326/M20-2945.