Baseline Outcome Rates
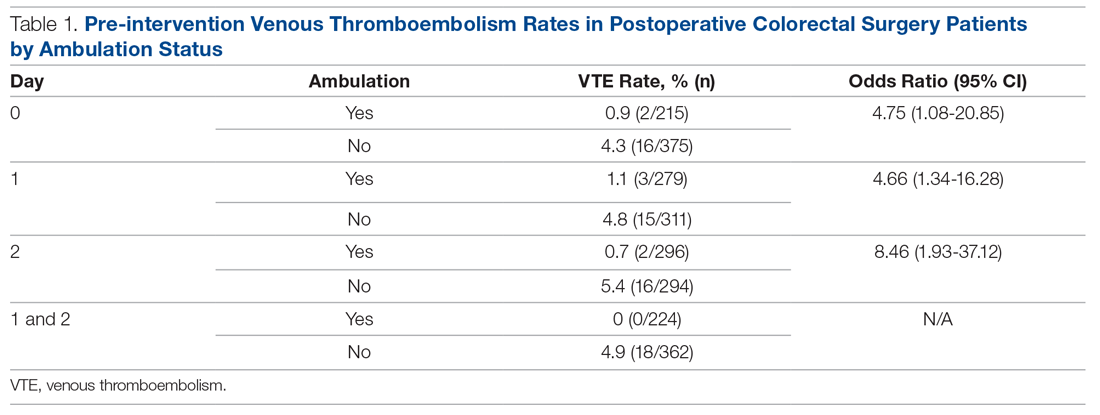
A total of 1762 patients were identified during the pre-intervention period. The overall VTE rate in the pre-intervention group was 2.7% (n = 48), with 39 DVTs (2.2%) and 13 PEs (0.7%). Pre-intervention ambulation data were available on 590 patients. Baseline ambulation rates on PODs 0, 1, and 2 were 36.4% (213/590), 47.3% (279/590), and 50.2% (296/590), respectively. Patients who did not ambulate on POD 0 had a VTE rate of 4.3%, as compared to 0.9% in those who did ambulate (Table 1). Patients who did not ambulate twice on POD 1 had a VTE rate of 4.8%, compared to 1.1% in those who did ambulate (odds ratio [OR], 4.66; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34 to 16.28). Patients who did not ambulate twice on POD 2 had a VTE rate of 5.4%, compared to 0.7% in those who did. Finally, those who ambulated twice on both PODs 1 and 2 had a 0% rate of VTE, compared to 4.9% in those who did not ambulate on both PODs.
Ambulation Protocol
After baseline outcome rates had been established, a multidisciplinary team of medical assistants, nurses, nurse practitioners, and physicians worked together to identify all processes that involved postoperative ambulation. Given the significant differences in VTE rates between patients who ambulated and those that did not, we created a multidisciplinary ambulation protocol using the PDSA method.14 Multiple points of patient contact were chosen for intervention, and the ambulation protocol was implemented in June 2018 and continued for 7 months.
Patients were observed from their initial office visit with a surgeon, during the preoperative education encounter, and in the operating room and on the surgical ward until discharge. Representatives from multiple disciplines who encountered patients at various times in the process, including medical assistants, patient care technicians, nurses, nurse practitioners, physical therapists, and physicians, participated in a kick-off meeting to identify difficulties they encounter when encouraging patient ambulation. The following 4 areas were identified.
Barriers to Patient Ambulation
Patient Expectations. Patients did not appear to have a clear expectation of what their ambulation goals were postoperatively, despite the fact that each patient is given an operative pathway booklet that includes their goals for each day, including ambulation. The consensus was that patients were overwhelmed with the amount of information and, oftentimes, the severity of their diagnosis, so the information regarding ambulation was not retained. Nurses commented that patients frequently stated that they did not think their surgeon wanted them to get out of bed postoperatively.
Electronic Orders. There was confusion within the nursing staff regarding orders in the electronic health record compared to physician expectations. Orders stated patients should ambulate 3 times daily, but did not specify on which postoperative day this should start. Often, nursing verbal sign-out from the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) would be an order for bedrest, despite no clear origin of this order. This created confusion among the nursing staff as to what the appropriate ambulation orders should be.