Autism may begin in utero, based on a study of postmortem brain tissue from children with and without autism.
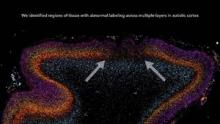
Patchy defects were noted in the six cellular layers of the cortex from 10 of 11 children with autism and from 1 of 11 unaffected children, based on gene expression studies performed on postmortem brain tissue from children aged 2-15 years at death. Abnormal laminar cytoarchitecture and cortical disorganization of neurons, but not of glia, were noted, according to Rich Stoner, Ph.D., of the Autism Center of Excellence at the University of California, San Diego, and his colleagues.
The findings, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, imply that layer formation and layer-specific neuronal differentiation are dysregulated during prenatal development.
The study results suggest that early recognition and treatment of autism may allow the developing brains of autistic children to construct alternative brain pathways around the patchy defects in the cortex. The result could be improved social functioning and communication, the researchers suggested (N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;370:1209-19 [doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1307491]).
In their study, Dr. Stoner and his colleagues used gene expression to examine cellular markers in each of the cortical layers as well as genes that are associated with autism. Markers for several layers of the cortex were absent in the brain tissue of 10 of 11 (91%) children with autism and in 1 of 11 (9%) control children. The areas of disorganization were seen in multiple cortical layers, with most abnormal expression noted in layers 4 and 5 and focal disruption of cortical laminar architecture as patches that were 5-7 mm long.
The research was supported by grants from a variety of nonprofit organizations. Tissue for the study was provided by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development’s Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders, the Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders, the Autism Tissue Program, and the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center.
On Twitter @maryjodales