Clinical Review
Get smart about dense breasts
An expert radiologist and dense breast educators address specific questions that will arise in your counseling and care of women who are...
Janelle Yates, Senior Editor
The contributors to this article report no relevant financial relationships.

“I believe the overall ACS mammography benefit evidence synthesis is reasonable and is in keeping with both NCCN and ACOG’s current recommendations. NCCN and ACOG mammography screening recommendations have both valued lives saved more highly than the ‘harms’ such as recalls and needle biopsies,” Dr. Pearlman says.
“If one combines ACS ‘strong’ and ‘qualified’ recommendations, ACS recommendations are similar to current ACOG and NCCN recommendations for mammography,” he adds.
Dr. Pearlman finds 7 areas of agreement between NCCN/ACOG and ACS recommendations, using both strong and qualified recommendations:
Where the ACS and ACOG/NCCN disagree is over the issue of the physical exam (abandoning CBE in average-risk women).
In regard to this last item, Dr. Pearlman says, “The ACS made a qualified recommendation against clinical breast exam. There is no high-level data to support such a marked change in practice. For example, when recommendations against breast self-examinations (BSE) were made, there were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) showing a lack of benefit and significant harms with BSE. With RCT-level data, it made sense to make a recommendation against the long-taught practice of SBE in average-risk women. That was not the case here. In fact, there are small amounts of data showing benefits of clinical breast exam.”
“One of my biggest concerns is not just the recommendation against CBE,” says Dr. Pearlman, “but that this may lead many women to interpret [this statement] as if they do not need to see their health care provider anymore. As you may recall, the American College of Physicians (ACP) recommended against annual pelvic examinations in asymptomatic patients. The ACS recommendation statement—taken together with the ACP statement—basically suggests that average-risk women don’t ever need to see a provider for a pelvic or breast examination except every 5 years for a Pap smear. That thinking does not recognize the importance of the clinical encounter (not just the CBE or pelvic exam), which is the opportunity to perform risk assessment and provide risk-reduction recommendations and healthy lifestyle recommendations.”
Radiologists resist new recommendations
Although the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the Society of Breast Imaging (SBI) agree with the ACS that mammography screening saves lives and should be available to women aged 40 and older, the 2 imaging organizations continue to recommend that annual screening begin at age 40. Their rationale: The latest ACS breast cancer screening guidelines, and earlier data used by the USPSTF to create its recommendations, both note that starting annual mammography at age 40 “saves the most lives.”
Where the organizations differ from the ACR is summed up by a formal statement on the ACR Web site: “The ACR and SBI strongly encourage women to obtain the maximum lifesaving benefits from mammography by continuing to get annual screening.”4
When OBG Management touched base with radiologist Barbara Monsees, MD, professor of radiology and Evens Professor of Women’s Health at Washington University Medical Center in St. Louis, Missouri, she expressed dismay at early news reports on the ACS guidelines.
“I’m dismayed that the headlines don’t seem to correlate with what the ACS actually recommended. The ACS did not state that women should wait until age 45 to begin screening. I believe the ACS was going for a more nuanced approach, but since that’s a bit complicated, I think that reporters have misconstrued what was intended,” Dr. Monsees says.
“The ACS guideline says that women between 40 and 44 years should have the opportunity to begin annual screening,” she says, noting that this recommendation was graded as “qualified.”
“The ACS states that a qualified recommendation indicates that ‘there is clear evidence of benefit of screening, but less certainty about the balance of benefits and harms, or about patients’ values and preferences, which could lead to different decisions about screening.’” The guideline also articulates the view “that the meaning of a qualified recommendation for patients is that the ‘majority of individuals in this situation would want the suggested course of action, but many would not.’ Therefore, I find it mind-boggling that this has been interpreted to mean that women should not begin screening until age 45.”1
“It is my opinion that it is clear that if women want to achieve the most lifesaving benefit from screening, they should adhere to a schedule of yearly mammograms beginning at age 40,” says Dr. Monsees. However, she also agrees with the ACS notation that clinicians should acknowledge that “different choices will be appropriate for different patients and that clinicians must help each patient arrive at a management decision consistent with her values and preferences.”1

An expert radiologist and dense breast educators address specific questions that will arise in your counseling and care of women who are...
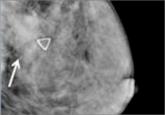
What will you tell your patient who asks about the clinical significance of dense breasts detected on her mammogram? Here I offer my current...
The authors of this prospective study involving more than 350,000 patients observed high interval cancer rates for women with 5-year breast cancer...
The benefit is small and the cost is high, according to this comparative modeling study.
