Clinical Review
Zika virus: Counseling considerations for this emerging perinatal threat
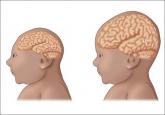
Zika virus infection, although typically mild and often asymptomatic, can have serious consequences in pregnancy. As the pandemic rapidly spreads...
Anushka Chelliah, MD, and Patrick Duff, MD


The authors report no financial relationships relevant to this article.

The ZV can be transmitted by sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.15 It is known to persist longer in semen than in blood or urine, though the exact duration remains unknown. Atkinson and colleagues16 reported RT-PCR detection of ZV RNA in semen about 62 days after onset of febrile illness—long after the virus became undetectable in blood.15
Mansuy and colleagues17 found that the viral load in semen was more than 100,000 times that in blood and urine more than 2 weeks after symptom onset.16 The ZV has been detected in saliva, urine, and breast milk. Although it has not been identified in vaginal secretions in humans, it has been detected in the vaginal secretions of nonhuman primates up to 7 days after subcutaneous inoculation of virus.18 In addition, the first case of female-to-male sexual transmission of ZV infection was just reported.19 In this report, transmission seems to have occurred on day 3 of the woman’s symptomatic illness, when she had unprotected vaginal intercourse with her partner. The partner became symptomatic 7 days after sexual exposure. To date, there is no evidence that infection is spread through kissing or breastfeeding.
The most recent recommendations from the CDC are that a man with symptomatic ZV infection wait at least 6 months before having unprotected sexual contact. In addition, a man who is asymptomatic after ZV exposure should wait at least 8 weeks before having unprotected sexual contact.17
A woman planning a pregnancy should know there is no evidence that prior ZV infection increases the risk of birth defects. However, a woman with a proven ZV infection should wait at least 8 weeks after symptom onset before trying to conceive. Even an asymptomatic woman with possible exposure should wait at least 8 weeks after the last exposure before attempting conception. In addition, given the risks associated with maternal and fetal infection, a man who has been exposed to the virus and who has a pregnant partner should abstain from unprotected sexual contact for the duration of the pregnancy.20
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.

Zika virus infection, although typically mild and often asymptomatic, can have serious consequences in pregnancy. As the pandemic rapidly spreads...

Physicians have requested information about which insect repellents to recommend to help pregnant women avoid Zika and other mosquito-born...
Recent studies offer new data on treatments for surgical-site infections after cesarean delivery, postpartum endometritis, and chlamydia infection...
Which infections affect women more adversely during pregnancy, and how can risk of exposure to these infections be diminished?
