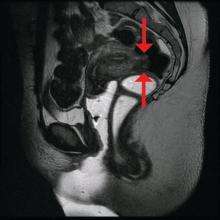
Segmental resection has been associated with significant postoperative complications. In a single-center series of 436 laparoscopic colorectal resections for deep infiltrating endometriosis, rectovaginal and anastomotic fistula were among the most frequent postoperative complications (3.2% and 1.1%), along with transient urinary retention, which occurred in almost 20% (Surg Endosc. 2010 Jan;24:63-7).
Patients undergoing discoid resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis also had a significantly lower rate of temporary ileostomy (2.1% vs. 9.1%), a reduced rate of postoperative fever, and a reduced rate of gastrointestinal complications, mainly anastomotic leak or rectovaginal fistula (2.1% vs. 5.6%). There were no significant differences in the recurrence rate (13.8% vs. 11.5%).
A retrospective cohort study from our institution similarly showed decreased operative time, blood loss, hospital stay, and a lower rate of anastomotic strictures in patients who underwent laparoscopic anterior discoid resection between 2001 and 2009. The ADR group consistently had higher increments of improvement in bowel symptoms and dyspareunia, compared with patients who were selected to have segmental resection. Patients were followed for a mean of 41 months (JSLS. 2011;15[3]:331-8).