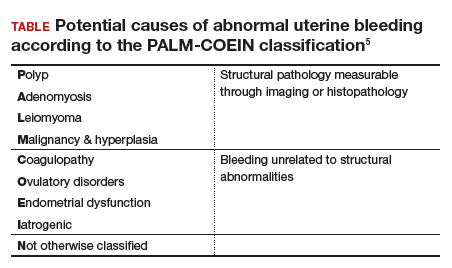
Dr. Sanfilippo: I encourage residents to go through an orderly sequence of assessment for evaluating abnormal uterine bleeding, including anatomic and endocrinologic factors. The PALM-COEIN classification system is a great mnemonic for use in evaluating abnormal uterine bleeding (TABLE).5 Is there a role for an aid such as PALM-COEIN in your practice?
Dr. Bradley: I totally agree. In 2011, Malcolm Munro and colleagues in the FIGO Working Group on Menstrual Disorders helped us to have a reporting on outcomes by knowing the size, number, and location of fibroids.5 This helps us to look for structural causes and then, to get to the answer, we often use imaging such as ultrasonography or saline infusion, sometimes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), because other conditions can coexist—endometrial polyps, adenomyosis, and so on.
The PALM-COEIN system helps us to look at 2 things. One is that in addition to structural causes, there can be hematologic causes. While it is rare in a 24-year-old, we all have had the anecdotal patient who came in 6 months ago, had a fibroid, but had a platelet count of 6,000. Second, we have to look at the patient as a whole. My residents, myself, and our fellows look at any bleeding. Does she have a bleeding diathesis, bruising, nose bleeds; has she been anemic, does she have pica? Has she had a blood transfusion, is she on certain medications? We do not want to create a “silo” and think that the patient can have only a fibroid, because then we may miss an opportunity to treat other disease states. She can have a fibroid coexisting with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), for instance. I like to look at everything so we can offer appropriate treatment modalities.
Dr. Sanfilippo: You bring up a very important point. Coagulopathies are more common statistically at the earlier part of a woman’s reproductive age group, soon after menarche, but they also occur toward menopause. We have to be cognizant that a woman can develop a coagulopathy throughout the reproductive years.
Dr. Anderson: You have to look at other medical causes. That is where the PALM-COEIN system can help. It helps you take the blinders off. If you focus on the fibroid and treat the fibroid and the patient still has bleeding, you missed something. You have to consider the whole patient and think of all the nonclassical or nonanatomical things, for example, thyroid disease. The PALM-COEIN helps us to evaluate the patient in a methodical way—every patient every time—so you do not miss something.
The value of MRI
Dr. Sanfilippo: What is the role for MRI, and when do you use it? Is it for only when you do a procedure—laparoscopically, robotically, open—so you have a detailed map of the fibroids?
Dr. Anderson: I love MRI, especially for hysteroscopy. I will print out the MRI image and trace the fibroid because there are things I want to know: exactly how much of the fibroid is inside or outside, where this fibroid is in the uterus, and how much of a normal buffer there is between the edge of that fibroid and the serosa. How aggressive can I be, or how cautious do I need to be, during the resection? Maybe this will be a planned 2-stage resection. MRIs are wonderful for fibroid disease, not only for diagnosis but also for surgical planning and patient counseling.
Dr. Bradley: SIS is also very useful. If the patient has an intracavitary fibroid that is larger than 4.5 to 5 cm and we insert the catheter, however, sometimes you cannot distend the cavity very well. Sometimes large intramural fibroids can compress the cavity, making the procedure difficult in an office setting. You cannot see the limits to help you as a surgical option. Although SIS generally is associated with little pain, some patients may have pain, and some patients cannot tolerate the test.
Continue to: I would order an MRI for surgical planning when...