CASE Continued: Workup
On physical exam, the patient’s breasts are noted to be cup size DDD and asymmetric, with the left breast larger than the right; there is no contour deformity. There is no skin or nipple retraction, skin rash, swelling, or nipple changes bilaterally. No dominant masses are appreciated bilaterally. Manual compression elicits no nipple discharge.
Although the discharge is nonbloody, its spontaneity, unilaterality, and single-duct/orifice origin suggest a pathologic cause. The patient is referred for breast imaging.
Imaging workup for pathologic discharge
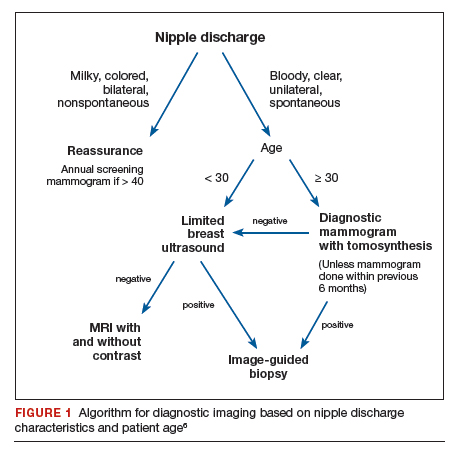
The American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria is a useful tool that provides an evidence-based, easy-to-use algorithm for breast imaging in the patient with pathologic nipple discharge (FIGURE 1).6 The algorithm is categorized by patient age, with diagnostic mammography recommended for women aged 30 and older.6 Diagnostic mammography is recommended if the patient has not had a mammogram study in the last 6 months.6 For patients with no prior mammograms, we recommend bilateral diagnostic mammography to compare symmetry of the breasts.
Currently, no studies show that digital breast tomosynthesis (3-D mammography) has a benefit compared with standard 2-D mammography in women with pathologic nipple discharge.6 Given the increased sensitivity of digital breast tomosynthesis for cancer detection, however, in our practice it is standard to use tomosynthesis in the diagnostic evaluation of most patients.
Mammography
On mammography, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) usually presents as calcifications. Both the morphology and distribution of calcifications are used to characterize them as suspicious or, typically, benign. DCIS usually presents as fine pleomorphic or fine linear branching calcifications in a segmental or linear distribution. In patients with pathologic nipple discharge and no other symptoms, the radiologist must closely examine the retroareolar region of the breast to assess for faint calcifications. Magnification views also can be performed to better characterize calcifications.
The sensitivity of mammography for nipple discharge varies in the literature, ranging from approximately 15% to 68%, with a specificity range of 38% to 98%.6 This results in a relatively low positive predictive value but a high negative predictive value of 90%.7 Mammographic sensitivity largely is limited by increased breast density. As more data emerge on the utility of digital breast tomosynthesis in dense breasts, mammographic sensitivity for nipple discharge will likely increase.
Ultrasonography
As an adjunct to mammography, the ACR Appropriateness Criteria recommends targeted (or “limited”) ultrasonography of the retroareolar region of the affected breast for patients aged 30 and older. Ultrasonography is useful to assess for intraductal masses and architectural distortion, and it has higher sensitivity but lower specificity than mammography. The sensitivity of ultrasonography for detecting breast cancer in patients presenting with nipple discharge is reported to be 56% to 80%.6 Ultrasonography can identify lesions not visible mammographically in 63% to 69% of cases.8 Although DCIS usually presents as calcifications, it also can present as an intraductal mass on ultrasonography.
The ACR recommends targeted ultrasonography for patients with nipple discharge and a negative mammogram, or to evaluate a suspicious mammographic abnormality such as architectural distortion, focal asymmetry, or a mass.6 For patient comfort, ultrasonography is the preferred modality for image-guided biopsy.
For women younger than 30 years, targeted ultrasonography is the initial imaging study of choice, according to the ACR criteria.6 Women younger than 30 years with pathologic nipple discharge have a very low risk of breast cancer and tend to have higher breast density, making mammography less useful. Although the radiation dose from mammography is negligible given technological improvements and dose-reduction techniques, ultrasonography remains the preferred initial imaging modality in young women, not only for nipple discharge but also for palpable lumps and focal breast pain.
Mammography is used as an adjunct to ultrasonography in women younger than 30 years when a suspicious abnormality is detected on ultrasonography, such as an intraductal mass or architectural distortion. In these cases, mammography can be used to assess for extent of disease or to visualize suspicious calcifications not well seen on ultrasonography.
For practical purposes regarding which imaging study to order for a patient, it is most efficient to order both a diagnostic mammogram (with tomosynthesis, if possible) and a targeted ultrasound scan of the affected breast. Even if both orders are not needed, having them available increases efficiency for both the radiologist and the ordering physician.
Continue to: CASE Continued: Imaging findings...