Getting started
Physicians and their colleagues and staff first need to become comfortable with telemedicine technology. Physicians can begin by using video communication for other purposes, such as for conducting staff meetings. They should practice starting and ending calls and adjusting audio volume and video quality to ensure good reception.
Selecting a video platform
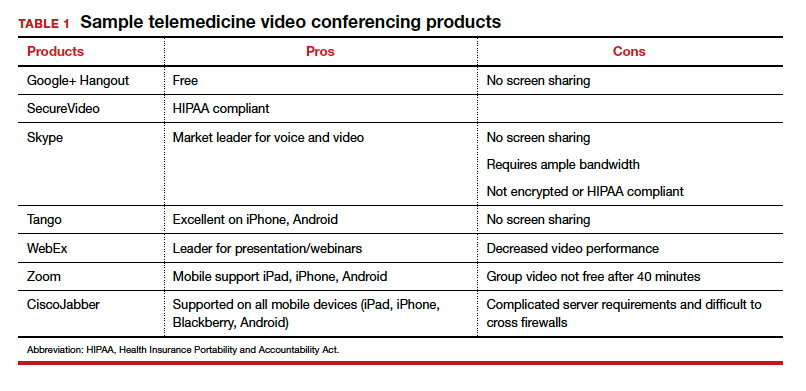
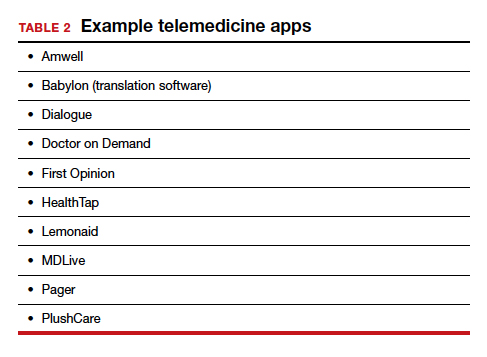
TABLE 1 provides a list of the most popular video providers and the advantages and disadvantages of each, and TABLE 2 shows a list of free video chat apps. Apps are available that can:
- share and mark up lab tests, magnetic resonance images, and other medical documents without exposing the entire desktop
- securely send documents over a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant video
- stream digital device images live while still seeing patients’ faces.
Physicians should make sure their implementation team has the necessary equipment, including webcams, microphones, and speakers, and they should take the time to do research and test out a few programs before selecting one for their practice. Consider appointing a telemedicine point person who is knowledgeable about the technology and can patiently explain it to others. And keep in mind that video chatting is dependent upon a fast, strong Internet connection that has sufficient bandwidth to transport a large amount of data. If your practice has connectivity problems, consider consulting with an information technology (IT) expert.
Testing it out and obtaining feedback
Once a team is comfortable using video within the practice, it is time to test it out with a few patients and perhaps a few payers. Most patients are eager to start using video for their medical encounters. Even senior patients are often willing to try consults via video. According to a recent survey, 64% of patients are willing to see a physician over video.3 And among those who were comfortable accepting an invitation to participate in a video encounter, increasing age was actually associated with a higher likelihood to accept an invite.
Physician colleagues, medical assistants, and nurse practitioners will need some basic telemedicine skills, and physicians and staff should be prepared to make video connections seamless for patients. Usually, patients need some guidance and encouragement, such as telling them to check their spam folder for their invites if the invites fail to arrive in their email inbox, adjusting audio settings, or setting up a webcam. In the beginning, ObGyns should make sure they build in plenty of buffer time for the unexpected, as there will certainly be some “bugs” that need to be worked out.
ObGyns should encourage and collect patient feedback to such questions as:
- What kinds of devices (laptop, mobile) do they prefer using?
- What kind of networks are they using (3G, corporate, home)?
- What features do they like? What features do they have a hard time finding?
- What do they like or not like about the video experience?
- Keep track of the types of questions patients ask, and be patient as patients become acclimated to the video consultation experience.
Continue to: Streamlining online workflow...