Providing counsel to patients
Patients often seek advice on how to choose vaginal moisturizers and lubricants. Understanding the compositions of these products and their scientific evidence is useful when helping patients make informed decisions regarding their pelvic health. Most commercially available lubricants are either water- or silicone- based. In one study comparing these two types of lubricants, water-based lubricants were associated with fewer genital symptoms than silicone-based products.14 Women may want to use a natural or organic product and may prefer plant-based oils such as coconut oil or olive oil. Patients should be counseled that latex condoms are not compatible with petroleum-, mineral oil- or plant oil-based lubricants.
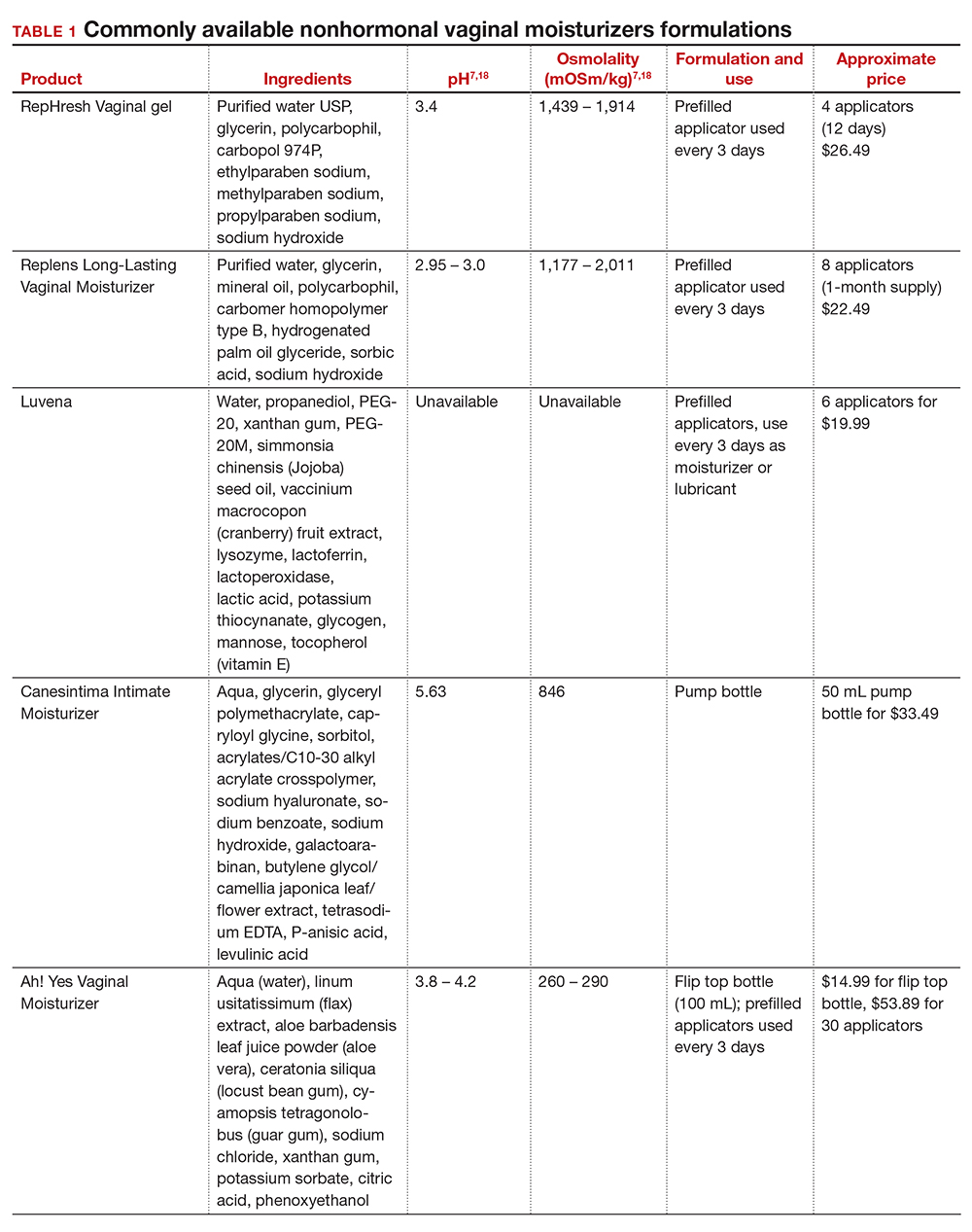
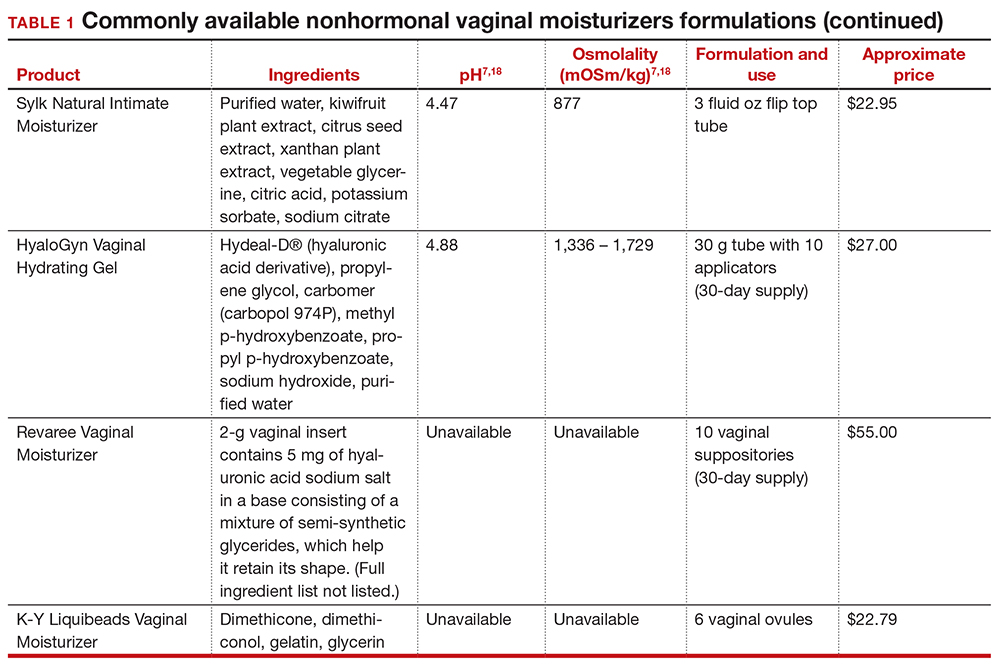
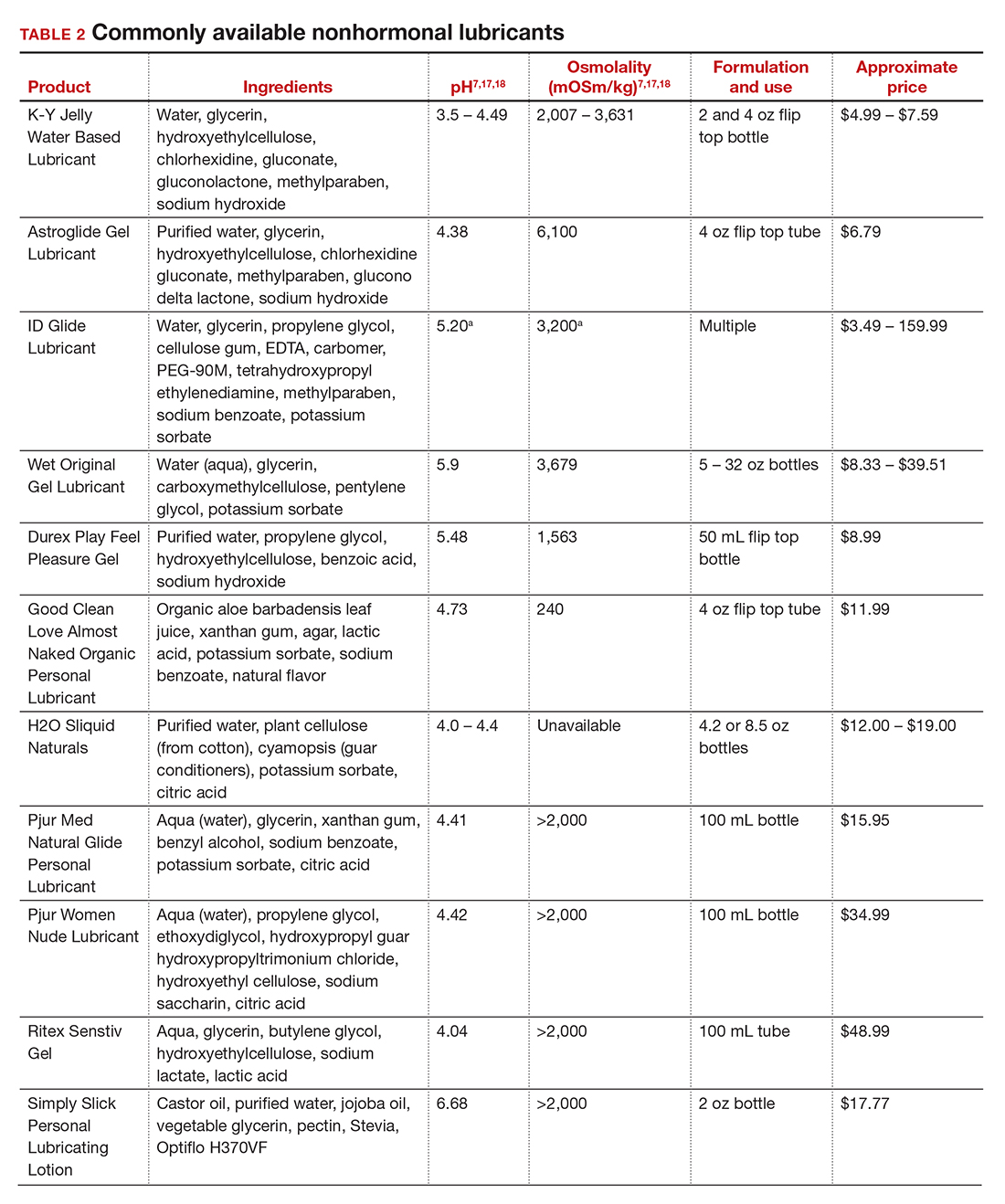
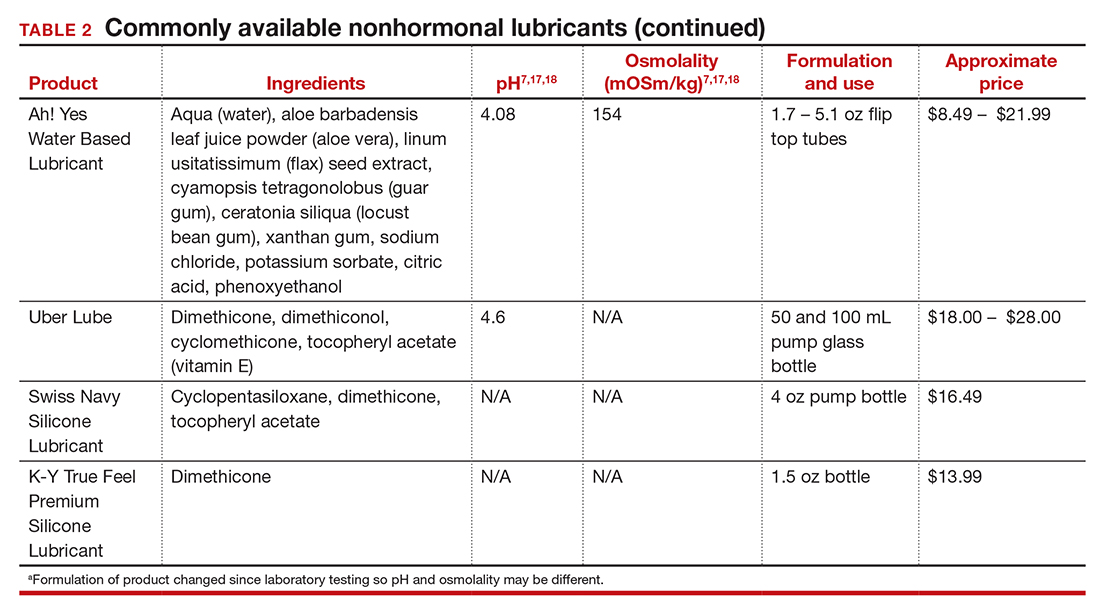
In our practice, we generally recommend silicone-based lubricants, as they are readily available and compatible with latex condoms and generally require a smaller amount than water-based lubricants. They tend to be more expensive than water-based lubricants. For vaginal moisturizers, we often recommend commercially available formulations that can be purchased at local pharmacies or drug stores. However, a patient may need to try different lubricants and moisturizers in order to find a preferred product. We have included in TABLES 1 and 27,17,18 a list of commercially available vaginal moisturizers and lubricants with ingredient list, pH, osmolality, common formulation, and cost when available, which has been compiled from WHO and published research data to help guide patient counseling.
The effects of additives
Water-based moisturizers and lubricants may contain many ingredients, such as glycerols, fragrance, flavors, sweeteners, warming or cooling agents, buffering solutions, parabens and other preservatives, and numbing agents. These substances are added to water-based products to prolong water content, alter viscosity, alter pH, achieve certain sensations, and prevent bacterial contamination.7 The addition of these substances, however, will alter osmolality and pH balance of the product, which may be of clinical consequence. Silicone- or oil-based products do not contain water and therefore do not have a pH or an osmolality value.
Hyperosmolar formulations can theoretically injure epithelial tissue. In vitro studies have shown that hyperosmotic vaginal products can induce mild to moderate irritation, while very hyperosmolar formulations can induce severe irritation and tissue damage to vaginal epithelial and cervical cells.19,20 The WHO recommends that the osmolality of a vaginal product not exceed 380 mOsm/kg, but very few commercially available products meet these criteria so, clinically, the threshold is 1,200 mOsm/kg.17 It should be noted that most commercially available products exceed the 1,200 mOsm/kg threshold. Vaginal products may be a cause for vaginal irritation and should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
The normal vaginal pH is 3.8–4.5, and vaginal products should be pH balanced to this range. The exact role of pH in these products remains poorly understood. Nonetheless, products with a pH of 3 or lower are not recommended.18 Concerns about osmolality and pH remain theoretical, as a study of 12 commercially available lubricants of varying osmolality and pH found no cytotoxic effect in vivo.18
Vaginal moisturizers and lubricants contain many inactive ingredients, the most controversial of which are parabens. These substances are used in many cosmetic products as preservatives and are weakly estrogenic. These substances have been found in breast cancer tissue, but their possible role as a carcinogen remains uncertain.21,22 Nonetheless, the use of paraben-containing products is not recommended for women who have a history of hormonally-driven cancer or who are at high risk for developing cancer.7 Many lubricants contain glycerols (glycerol, glycerine, and propylene glycol) to alter viscosity or alter the water properties. The WHO recommends limits on the content of glycerols in these products.17 Glycerols have been associated with increased risk of bacterial vaginosis (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 11.75; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.96–70.27), and can serve as a food source for candida species, possibly increasing risk of yeast infections.7,23 Additionally, vaginal moisturizers and lubricants may contain preservatives such as chlorhexidine, which can disrupt normal vaginal flora and may cause tissue irritation.7
Continue to: Common concerns to be aware of...