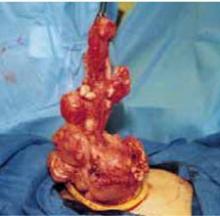
FIGURE 6 Hysterectomy for the large, solid, fibroid uterus
D. After trachelectomy, the large uterine specimen is removed by morcellation. Notice that the retractor is able to stretch significantly, allowing the exteriorization of uteri with diameters considerably larger than that of the retractor.
Devices that simplify the procedure
Occasionally, hysterectomy using traditional clamp, division, and suture ligation can be tedious, frustrating, and time-consuming, especially when exposure is limited or difficult. Several devices developed for laparoscopic surgery can ease suture ligation and the division of blood vessels, ligaments, and tissue bundles during minilaparotomy hysterectomy. They include the Hem-o-lok ligating clip (Weck Closure Systems); the LigaSure Atlas, a vessel sealer-divider (Valleylab, Tyco Healthcare, Boulder, Colo); the ETS 45-Flex endoscopic linear cutter (Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Cincinnati, Ohio); and the PK bipolar cutting forceps (Gyrus Medical, Maple Grove, Minn).
Additional concerns
Is the incision too large? Fears that incisions over 5 cm might nullify minimally invasive surgery’s benefits have proven unfounded.
Laparoscopic procedures that use a 7-cm to 8-cm incision to introduce the hand into the abdomen, as well as those performed in conjunction with minilaparotomy, have consistently failed to identify a link between these combinations and morbidity or lengthy recovery. A “large” minilaparotomy incision is still superior to a standard abdominal hysterectomy in terms of convalescence, and it is significantly faster and more cost-effective than a prolonged laparoscopic or laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy.3-10
Do any conditions contraindicate minilaparotomy? In patients with documented or strongly suspected severe pelvic conditions (for example, advanced endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, bowel disease, or malignancy), preliminary laparoscopic evaluation to determine the pathologic condition’s severity and extent is strongly recommended.
If during this assessment you detect pathology that is not appropriate for laparoscopic surgery or minilaparotomy, perform a traditional laparotomy. If, however, this evaluation demonstrates that pelvic pathology is amenable to laparoscopic surgery, a laparoscopic hysterectomy or laparoscopic-assisted minilaparotomy hysterectomy is indicated.
Dr. Pelosi II reports that he is a consultant for Apple Medical Corporation. Dr. Pelosi III reports no affiliations or financial arrangements with any of the manufacturers of products mentioned in this article or their competitors.