“Physical activity is a proven strategy for managing arthritis symptoms,” but 35% of Americans with arthritis do not participate in any such activities or exercise, according to investigators who analyzed data from a national survey of more than 440,000 adults.
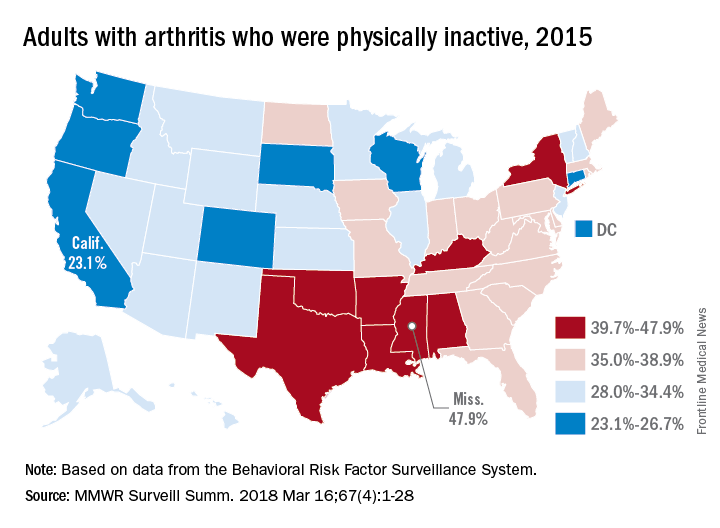
A look at estimated state-level participation in physical activity for 2015 shows that geographic disparities exist, with the highest inactivity rates seen mainly in southern states and higher rates generally found in the eastern half of the country. The highest rate of past-month physical inactivity, 47.9%, came in Mississippi, which was followed by Arkansas at 44.3% and Texas at 43.4%, Kamil E. Barbour, PhD, an epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s arthritis program, and his associates reported in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.The low rates of inactivity in the western half of the country were topped by California’s 23.1% and South Dakota’s 23.4%, with Oregon (24.0%) and Wisconsin (24.6%) not too far behind, Dr. Barbour and his associates said based on data for 441,456 adults aged 18 years and older who were interviewed for the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
Overall prevalence rates show that arthritis has the greatest effect in southern states, which, in addition to high inactivity, had more arthritis-attributable severe joint pain, more arthritis-attributable social participation restriction, and less leisure-time walking among adults with arthritis. This information, the investigators suggested, may help public health professionals “to better understand and target evidence-based nonpharmaceutical interventions, such as arthritis self-management education and physical activity.”
SOURCE: Barbour KE et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2018 Mar 16;67(4):1-28.