Take-Home Points
- There is no difference in PROMs following knotless or knotted labral repair.
- Operative time is shorter for knotless compared to knotted glenoid labral tears.
- Knotless constructs may be more predictable than knotted constructs biomechanically.
Orthopedic surgeons often encounter labral pathology, and labral tears historically have required open techniques. 1-3 Arthroscopy allows for advanced visualization and treatment of shoulder lesions, 4,5 including anterior, posterior, and superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions. 6
The goal of arthroscopic labral repair is to restore joint stability while maintaining range of motion. Arthroscopically repairing the labrum with suture anchors has become the standard technique, and several studies have reported satisfactory biomechanical and clinical results. 1,7-12 Surgeons traditionally have been required to tie knots for these anchors, but knot security varies significantly among experienced arthroscopic surgeons. 13 In addition, knots can migrate, 14 and bulky knots can cause chondral abrasion. 15,16 Several manufacturers have introduced knotless anchors for soft-tissue fixation. 15,17 The knotless technique provides a low-profile repair with potentially less operating time. 8 These factors may warrant switching from knotted to knotless techniques if outcomes are clinically acceptable. However, few studies have compared knotted and knotless techniques for glenohumeral labral repair. 8,15,18-21
We conducted a study to compare the clinical results and operative times of knotless and knotted fixation of anterior and posterior glenohumeral labral repairs and SLAP repairs. We hypothesized there would be no difference in patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) between knotted and knotless techniques.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated data that had been prospectively collected between 2012 and 2016 in a Surgical Outcomes System (SOS; Arthrex) database. Participation in this registry is elective, and enrollment can occur on a case-by-case basis. The database stores data on basic demographics, PROMs, and operative time. Data for our specific analysis were available for surgeries performed by 115 different surgeons. Inclusion criteria included primary isolated arthroscopic anterior, isolated posterior, and isolated SLAP repair with completely knotted or completely knotless labral repair and minimum 1-year follow-up. Exclusion criteria included hybrid knotted–knotless repair, rotator cuff repair, revision surgery, open surgery, and lack of complete follow-up data.
SOS is a proprietary registry that allows for the collection of basic patient demographics, diagnostic and operative data, and PROMs. PROMs in the SOS shoulder arthroscopy module include Veterans RAND 12-Item Health Survey (VR-12) mental health and physical health component summary scores, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) scores. For this study, PROMs were reviewed before surgery and 6 and 12 months after surgery. In addition, operative times of all procedures were collected.
For the analysis, completely knotted and completely knotless techniques were compared for anterior repair, posterior repair, and SLAP repair. A t test was used to compare the techniques on PROMs, and χ2 test was used to evaluate proportion differences. Statistical significance was set at P < .05.
Results
Anterior Labral Repairs
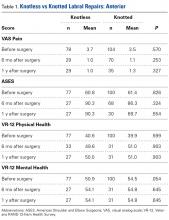
Of the 102 knotted anterior labral repairs that met the study criteria, 26 (25%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Of the 122 knotless labral repairs, 33 (27%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Seventy-five percent of knotted repairs and 80% of knotless repairs were performed in men. Mean (SD) age was 25.3 (11.7) years for the knotted group and 26.9 (10.6) years for the knotless group ( P = .109). Anterior labral repairs did not differ in PROMs at any point ( Table 1 ).
A mean of 2.8 anchors was used for knotted repairs, and a mean of 3.1 anchors was used for knotless repairs. Mean operative time was 75.8 minutes for knotted repairs and 67.5 minutes for knotless repairs. Mean (SD) time per anchor was 30.9 (13.9) minutes for knotted repairs and 25.6 (19.5) minutes for knotless repairs ( P = .021).
Posterior Labral Repairs
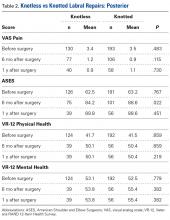
Of the 165 knotted posterior labral repairs that met the study criteria, 39 (29%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Of the 229 knotless labral repairs, 56 (24%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Eighty-five percent of knotted repairs and 74% of knotless repairs were performed in men. Mean (SD) age was 29.1 (12.0) years for the knotted group and 27.5 (11.9) years for the knotless group ( P = .148). Posterior labral repairs did not differ in PROMs before surgery or 1 year after surgery; 6 months after surgery, these repairs differed only in ASES scores ( Table 2 ).
A mean of 3.6 anchors was used for knotted repairs, and a mean of 3.0 anchors was used for knotless repairs. Mean operative time was 67.0 minutes for knotted repairs and 43.1 minutes for knotless repairs. Mean (SD) time per anchor was 21.1 (10.7) minutes for knotted repairs and 17.5 (14.7) minutes for knotless repairs ( P = .031).
SLAP Repairs
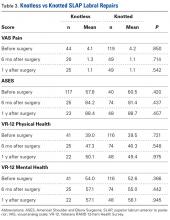
Of the 54 knotted SLAP repairs that met the study criteria, 24 (44%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Of the 138 knotless SLAP repairs, 48 (35%) had minimum 1-year follow-up. Seventy-two percent of knotted repairs and 72% of knotless repairs were performed in men. Mean (SD) age was 32.1 (11.6) years for the knotted group and 35.0 (12.8) years for the knotless group ( P = .246). SLAP repairs did not differ in PROMs at any point ( Table 3 ).
A mean of 1.9 anchors was used for knotted repairs, and a mean of 2.1 anchors was used for knotless repairs. Mean operative time was 59.0 minutes for knotted repairs and 40.9 minutes for knotless repairs. Mean (SD) time per anchor was 36.6 (22.4) minutes for knotted repairs and 26.3 (14.0) minutes for knotless repairs ( P = .080).
Discussion
Our hypothesis that there would be no difference in PROMs between knotted and knotless labral repairs was confirmed. Our findings are important because this study compared the gold standard of knotted suture anchor with the alternative knotless suture anchor in glenohumeral labral repair. These findings have several important implications for labral repair.
Knot tying traditionally has been used to achieve fixation with an anchor. Although simple in concept, knot tying can be challenging and its quality variable. Thal 15 wrote that good-quality arthroscopic suture anchor repair is difficult to achieve because satisfactory knot tying requires significant practice with certain devices designed specifically for knot tying. Multiple surgeons have noted a significant learning curve associated with knot tying, and there is no agreement on which knot is superior. 22-26 Leedle and Miller 17 even suggested that, because knot tying is difficult, tying knots arthroscopically can lead to knot failure. In their study, they concluded that the knot is consistently the weakest link in suture repair of an anterior labrum construct. In a controlled laboratory study, Hanypsiak and colleagues 13 found considerable knot-strength variability among expert arthroscopists. Only 65 (18%) of 365 knots tied fell within 20% of the mean for ultimate load failure, and only 128 (36%) of 365 fell within 20% of the mean for clinical failure (3 mm of displacement). These data suggested expert arthroscopists were unable to tie 5 consecutive knots of the same type consistently. Even among experts, it seems, knot strength varies significantly, and knot-strength issues may affect the rates of labral repair failure.
Multiple authors have also reported that bulky knots can cause chondral abrasion or that knots can migrate. 25,27 Rhee and Ha 27 reported that, when another knot (eg, a half-hitch knot) is tied to prevent knot failure, the resulting overall knot can be too bulky for a limited space, and chondral abrasion can result. In addition, regardless of size, a knot can migrate and, in its new position, start rubbing against the head of the humerus. Kim and colleagues 14 found that, even when a knot is placed away from the humeral head, migration and repeated contact with the head are possible. Park and colleagues 28 found that a significant number of knotted SLAP repairs required arthroscopic knot removal for relief of knot-induced pain and clicking.
Knotless constructs have several theoretical advantages over knotted constructs. Compared with a knotted technique, a knotless technique appears to provide more predictable strength, as variability in knot tying is eliminated (unpublished data). A knotless repair also has a lower profile,8 which should lead to less contact with the humeral head. 19 Last, a knotless repair is more efficient—it takes less time to perform. In our study, operative time was reduced by a mean of 5.3 minutes per anchor for anterior labral repair. Assuming a mean of 3 anchors, this reduction equates to 16 minutes per case. Therefore, a surgeon who performs 25 labral repairs a year can save 6.7 hours a year. Reduced operative time benefits the patient (ie, lower risk of infection and other complications 29), the surgeon, and the healthcare system (ie, cost savings). Macario 30 found that operating room costs averaged $62 per minute (range, $22-$133 per minute). Therefore, saving 16 minutes per case could lead to saving $992 per case. In summary, a knotless technique appears to be clinically and financially advantageous as long as its results are the same as or better than those of a knotted technique.
A few other studies have compared knotted and knotless techniques. In a cadaveric study, Slabaugh and colleagues 20 found no difference in labral height between traditional and knotless suture anchors. Leedle and Miller 17 found that knotless constructs are biomechanically stronger than knotted constructs in anterior labral repair. In a level 3 clinical study, Yang and colleagues 21 compared a conventional vertical knot with a knotless horizontal mattress suture in 41 patients who underwent SLAP repair. Functional outcome was no different between the 2 groups, but postoperative range of motion was improved in the knotless group. Ng and Kumar 31 compared 45 patients who had knotted Bankart repair with 42 patients who had knotless Bankart repair and found no difference in functional outcome or rate of recurrent dislocation. Similarly, Kocaoglu and colleagues 22 found no difference in recurrence rate between 18 patients who underwent a knotted technique for arthroscopic Bankart repair and 20 patients who underwent a knotless technique. Our findings corroborate the findings of these studies and further support the idea that there is no difference between knotted and knotless constructs with respect to PROMs.
Study Limitations
The major strength of this study was its large cohort and large population of surgeons. However, there were several study limitations. First, we could not detail specific repair techniques, such as simple or horizontal mattress orientation, and rehabilitation protocols and other variables are likely as well. Second, the repair technique was not randomized, and therefore there may have been a selection bias based on tissue quality. Although we cannot prove no bias, we think it was unlikely given that the groups were similar in age. Third, our data did not include information on range of motion or recurrent instability. Our goal was simply to evaluate PROMs among multiple surgeons using the 2 techniques. Fourth, there was substantial follow-up loss, which introduced potential selection bias. Last, there may have been conditions under which a hybrid technique with inferior knot tying, combined with a hybrid knotless construct, could have proved advantageous.
Conclusion
Our data showed that the advantages of knotless repair are not compromised in clinical situations. Although the data showed no significant difference in clinical outcomes, knotless repairs may provide surgeons with shorter surgeries, simpler constructs, less potential for chondral damage, and more consistent suture tensioning. Additional studies may further confirm these results.