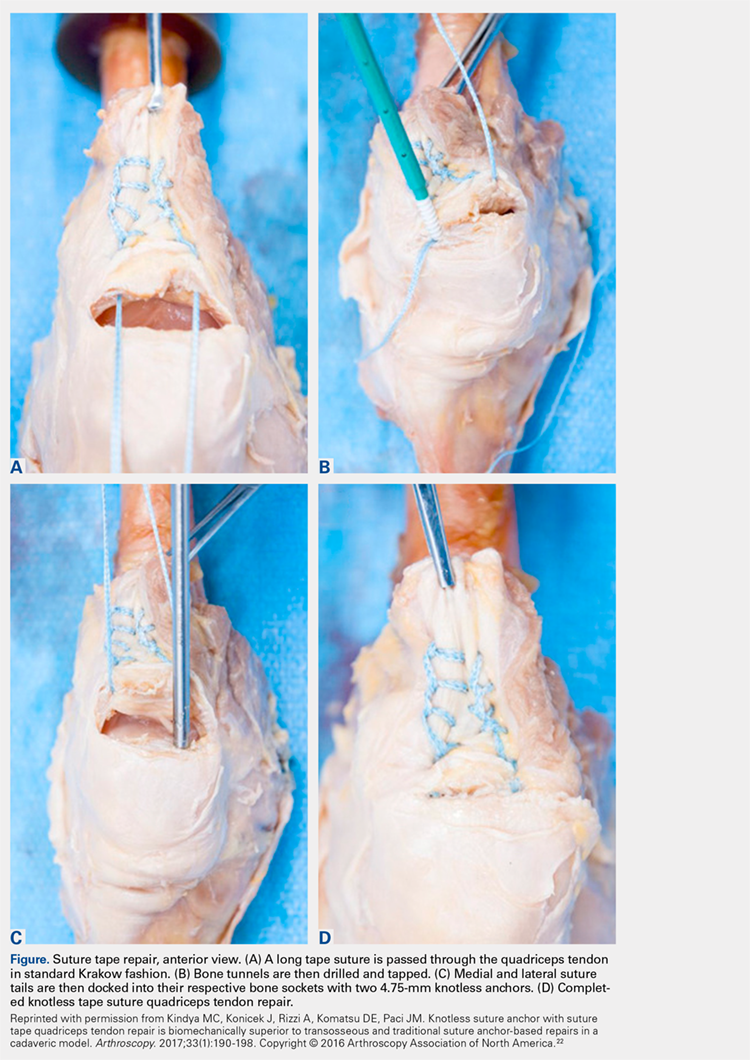
The proximal pole of the patella is then prepared by débriding any remaining soft tissue back to an area of exposed subcortical bone, which is débrided to a bleeding bony bed. Holes are drilled in the medial and lateral thirds of the patella at the proximal pole using the drill for 4.75-mm biocomposite knotless suture anchors (SwiveLock; Arthrex). The tap for the 4.75-mm anchors is then passed at each guide hole. In hard bone, double-tapping is recommended.
Next, the medial strand of tape suture is loaded within a 4.75-mm biocomposite knotless suture anchor eyelet and reduced to the patella. The medial anchor is malleted and screwed into place, while tension is kept on the lateral strand with the knee in full extension. The lateral strand is then placed into its 4.75-mm biocomposite knotless suture anchor, reduced to the patella, and then malleted and screwed into place in the lateral hole, thereby completing the core portion of the repair (Figures A-D). The core strands from the 4.75-mm biocomposite knotless suture anchors are then back-passed in mattress fashion and tied, and medial and lateral retinacular repairs are then performed using supersuture tape (SutureTape or FiberWire; Arthrex).
After surgery, the patient is placed in a knee brace locked in full extension and allowed to weight-bear as tolerated using crutches. During the first week, knee ROM is allowed up to 30°. During weeks 2 to 6 passive ROM is gradually increased to 90°, and use of crutches is tapered. At week 6 the brace is unlocked for ambulation; it may be discontinued after 7 to 8 weeks or when determined safe. Light activity is permitted from month 4 to month 6. A patient who achieves satisfactory strength, is clinically examined, and progresses through rehabilitation is allowed to return to fully unrestricted sport.
DISCUSSION
Quadriceps tendon rupture is an uncommon clinical entity that requires early surgical management.1-5,12,17,19 The standard of care is passage of nonabsorbable sutures through transosseous patellar bone tunnels, but repair with suture anchors has been studied as an alternative that allows for less tissue trauma, decreased operative time, safe early initiation of rehabilitation protocols, and reduced risk of patella fracture or damage.3,7,10-12,18-20,21,23 Despite these potential advantages, biomechanical studies have yielded inconsistent results regarding the superiority of suture anchor repair over repair with transosseous tunnels.7,10-12,18-20 We propose quadriceps tendon repair using the 4.75-mm biocomposite knotless suture anchor with tape suture technique as a biomechanically superior alternative to either transosseous tunnels or suture anchor repair alone, with significant advantages both in and out of the operating room.
Results of biomechanical studies comparing transosseous tunnel repair and standard suture anchor repair have been mixed, though the heterogeneity of their study methods and endpoints makes direct comparisons difficult.7,10-12,18-20 Petri and colleagues10 and Sherman and colleagues21 reported statistically significant higher load to failure10 and reduced gapping during cyclic loading10,21 with suture anchor repair relative to transosseous repair. However, Hart and colleagues12 found that repair with suture anchors had lower ultimate tensile load, and they concluded that transosseous repair is superior. Lighthart and colleagues11 found no significant difference in displacement between the 2 repairs.
Continue to: In our cadaveric biomechanical study...