Most non-traumatic injuries to the popliteal artery are iatrogenic and may occur during total knee replacement,1-8 high tibial osteotomy,2,3,5-7 anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction,2,6 posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction,2,6,9,10 and arthroscopic meniscectomy.2,6,9 Despite the rare occurrence of complications involving the popliteal artery during such procedures, results of vessel injuries can be devastating and may also lead to malpractice litigation. Anatomic variations of the distal popliteal artery and its significance in surgery have been well documented in the literature.2-6,8,11 However, due to lack of awareness, this issue is often unintentionally disregarded. We present the case of an aberrant anterior tibial artery that was found during the review of a magnetic resonance imaging study. The patient was provided written informed consent for print and electronic publication of this case report.
CASE
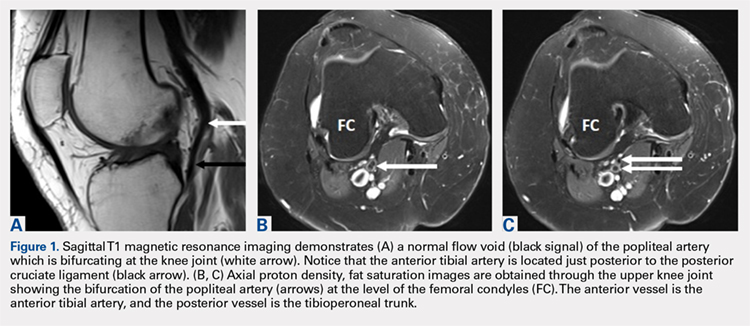
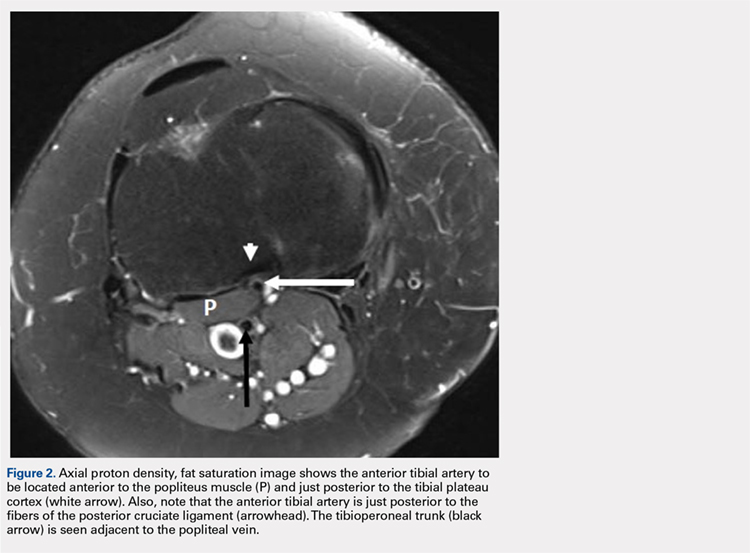
A 61-year-old woman presented with a history of right knee pain from osteoarthritis that had rapidly progressed over 1 week secondary to a fall. The patient had no history of previous knee surgery. After careful evaluation of her right knee pain, treatment options were discussed. The patient agreed to proceed with total knee arthroplasty (TKA). During preoperative planning, the patient’s previous magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was reviewed. The MRI study revealed an aberrant anterior tibial artery. The popliteal artery bifurcated at the level of the knee joint (Figures 1A-1C). After the bifurcation, the anterior tibial artery coursed anteriorly to the tibioperoneal trunk. The anterior tibial artery is seen just anterior to the popliteus muscle and just posterior to the tibial plateau cortex (Figure 2). Intraoperatively, an oscillating saw was utilized for the tibial cut. Care was taken not to penetrate the posterior cortex. An osteotome was used to elevate the tibial cut and hinge it open, and with a small mallet, finish the tibial cut. The patient had a successful TKA without complication.
DISCUSSION
Emerging from the adductor hiatus (Hunter’s canal), the normal course of the popliteal artery is a position slightly lateral in the intercondylar fossa. It courses obliquely and posteriorly to the popliteus then bifurcates into the anterior tibial artery and the tibioperoneal trunk at the inferior border of the popliteus. The tibioperoneal trunk bifurcates into both the posterior tibial artery and the peroneal artery at the proximal tibia well below the knee joint.
There are many reported cases of popliteal artery variations.2,3,6,7,9,11-13 Variations in the popliteal artery are consequences of persistent embryonic vessels from primitive segments of the artery or abnormal fusions among them.14 According to Kim and colleagues,11 variations can be classified by the modified Lippert’s system. This system has 3 categories with 3 subtypes (Table). Variations are not uncommon and occur in 7.4% to 12% of the population.2,4,5,7,13
Table. Modified Lippert’s System11
Category (Subtype) | |
I | Normal level of popliteal arterial branching |
IA | Usual pattern |
IB | Trifurcation- No true tibioperoneal trunk |
IC | Anterior tibioperoneal trunk- Posterior tibial artery is first branch |
II | High division of popliteal artery |
IIA | Anterior tibial artery arises at or above the knee joint |
IIB | Posterior tibial artery arises at or above the knee joint |
IIC | Peroneal artery arises at or above the knee joint |
III | Hypoplastic or aplastic branching with altered distal supply |
IIIA | Hypoplastic-aplastic posterior tibial artery |
IIIB | Hypoplastic-aplastic anterior tibial artery |
IIIC | Hypoplastic-aplastic posterior and anterior tibial artery |
Of these variations, type IIA, a high bifurcation of the anterior tibial artery, arising at or above the knee joint from the popliteal artery is the most significant. Forty-two percent of these vessels course anterior to the popliteus and make direct contact with the cortex of the posterior tibia.4 It is also the most frequent variant type reported in 1.2% to 6% of the population.3,7,11-13
Continue to: Injury to the popliteal artery...